金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.215,15 Aug. 2021(下)
2021-12-11 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文15篇,涵盖了高温合金、马氏体、铝合金等,国内科研单位包括上海交通大学、中国科学院金属研究所等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 215 目录
1. Predicting shear transmission across grain boundaries with an iterative stress relief model
用迭代应力消除模型预测跨晶界的剪切力传递
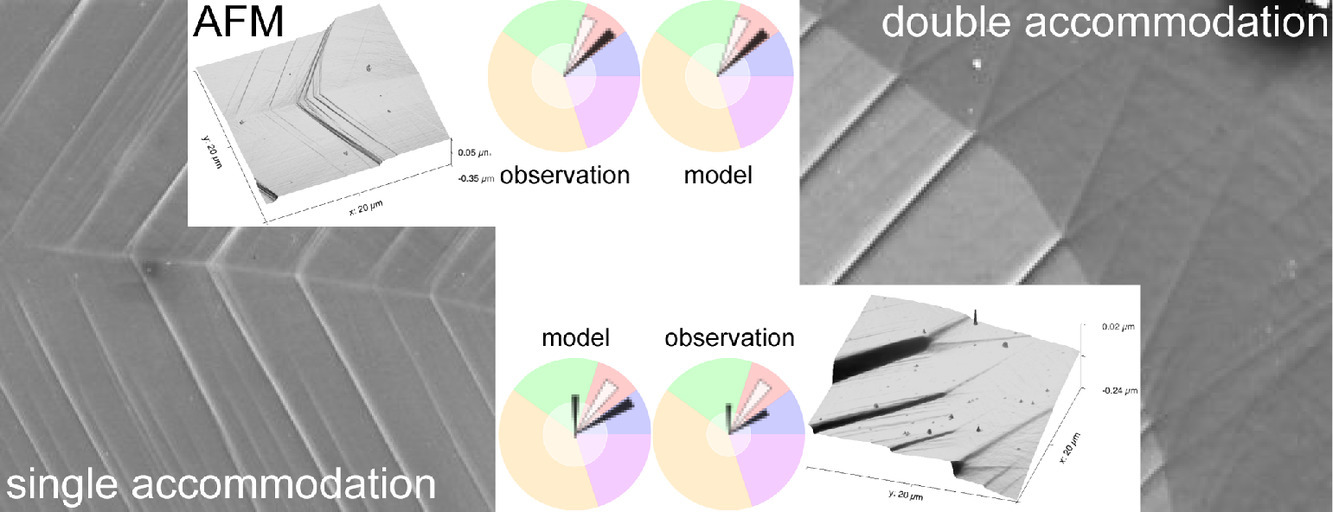
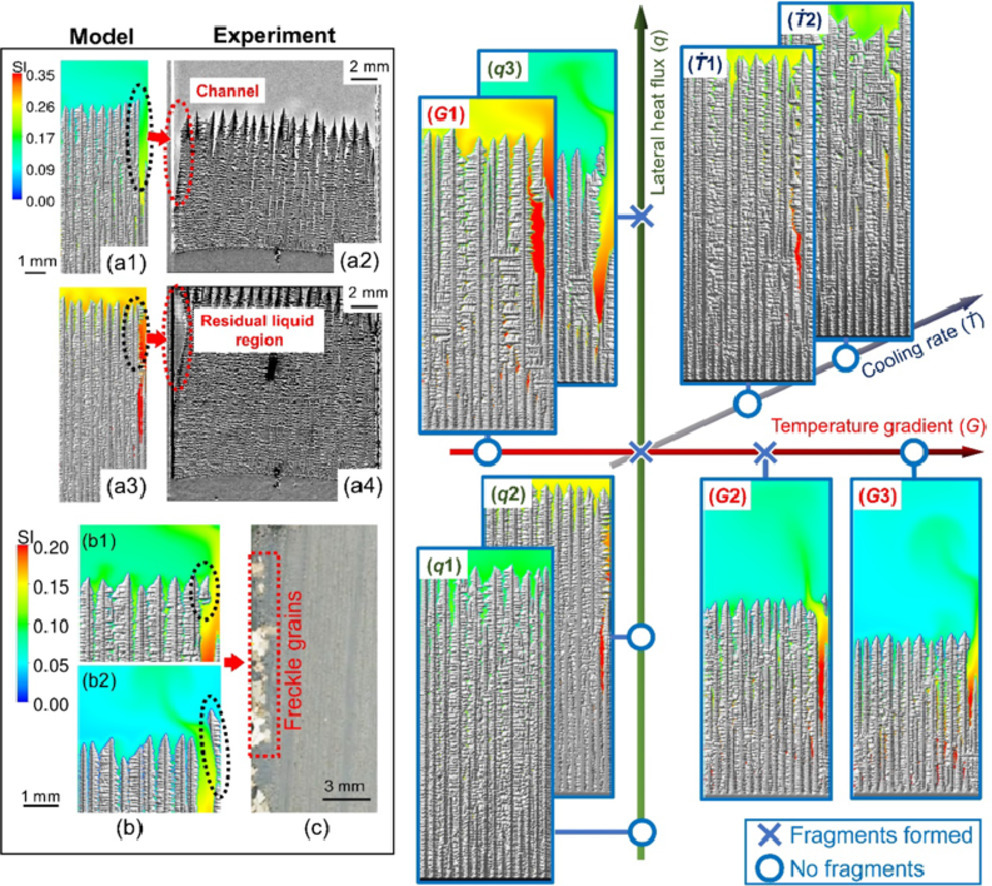
2. Solute enrichment induced dendritic fragmentation in directional solidification of nickel-based superalloys
镍基高温合金定向凝固中溶质富集诱发的枝晶碎裂
3. Controlling martensitic transformation characteristics in defect-free NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated using laser powder bed fusion and a process optimization framework
利用激光粉末床熔合技术制造的无缺陷 NiTi形状记忆合金中的马氏体相变特征的控制及工艺优化框架
4. Chemical short range order strengthening in BCC complex concentrated alloys
BCC复杂浓缩合金中的化学短程秩序强化
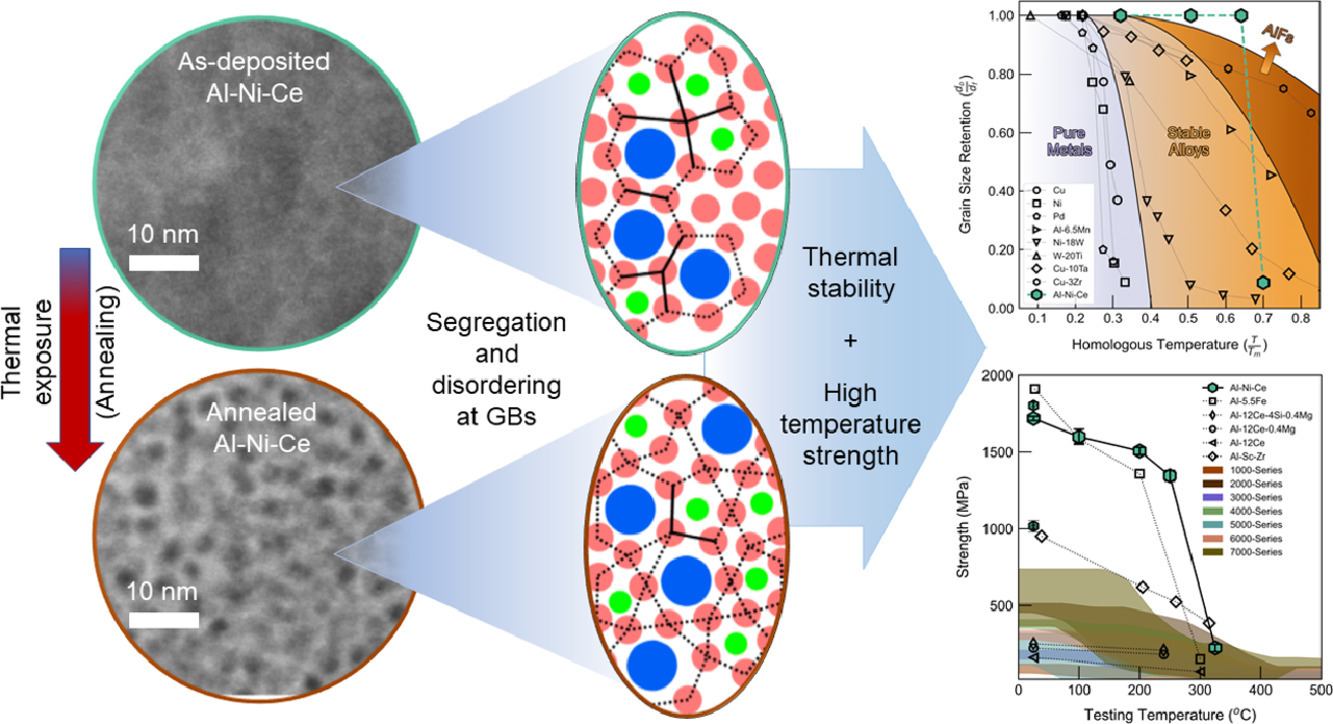
5. Disordered interfaces enable high temperature thermal stability and strength in a nanocrystalline aluminum alloy
无序界面使纳米晶铝合金具有高温热稳定性和强度
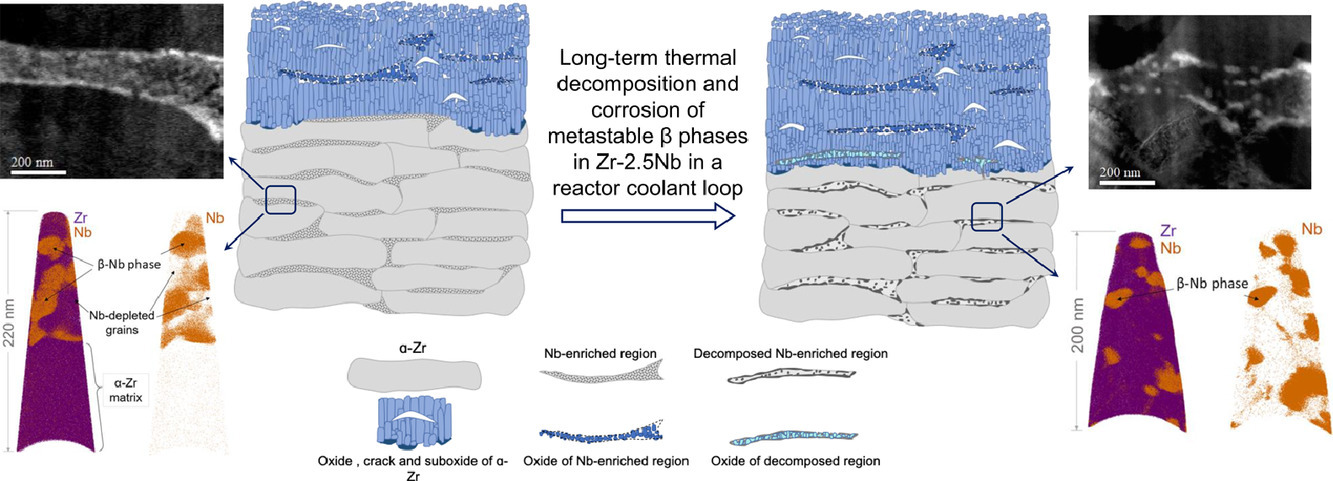
6. The role of β-Zr in a Zr-2.5Nb alloy during aqueous corrosion: A multi-technique study
β-Zr在 Zr-2.5Nb合金水腐蚀中的作用: 多技术研究
7. Natural and artificial ageing in aluminium alloys – the role of excess vacancies
铝合金的自然老化和人工老化--过剩空位的作用
8. Anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard free energy and interfacial energies for binary alloys with pairwise interactions
具有成对相互作用的二元合金的各向异性卡恩-希利亚德自由能和界面能
9. In-situ investigation of strain partitioning and microstructural strain path development up to and beyond necking
在颈缩前后的应变分配和微观应变路径发展的原位研究
10. An understanding of duplex microstructures encountered during high strength aluminium alloy laser beam melting processing
对高强度铝合金激光束熔炼加工过程中遇到的双相微结构的理解
11. Graphene supported MgNi alloy nanocomposite as a room temperature hydrogen storage material – Experiments and theoretical insights
石墨烯负载的镁镍合金纳米复合材料作为室温储氢材料--实验和理论的见解
12. Spinodal Decomposition in Nanocrystalline Alloys
纳米晶合金中的亚稳分解现象
13. Influence of solidification structure on austenite to martensite transformation in additively manufactured hot-work tool steels
凝固结构对增材制造热作工具钢中奥氏体向马氏体转变的影响
14. The nature of the maximum microhardness and thickness of the gradient layer in surface-strengthened Cu-Al alloys
表面强化的 Cu-Al合金中最大显微硬度的性质和梯度层的厚度的本质
15. Slip localization in Inconel 718: A three-dimensional and statistical perspective
718合金中的滑移定位:三维和统计角度
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 116992
1. Predicting shear transmission across grain boundaries with an iterative stress relief model
用迭代应力消除模型预测跨晶界的剪切力传递
Yang Su, Songyang Han, Philip Eisenlohr, Martin A.Crimp✉
Martin A.Crimp: crimp@egr.msu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116992
摘要
本文提出了一个新的模型来定量预测在晶界容纳冲击滑移的具体形变系统活动。该模型采用迭代方法,依次确定最多三个包容滑移系统和它们的相对剪切力。这个迭代应力释放模型的结果主要由晶界中Burgers矢量的连续性和晶界上冲击应力张量的迭代演变所控制。该模型通过比较预测22个不同的α-Ti剪切调节的观察结果进行了测试,并且这些观察结果是通过定向滑移轨迹分析和原子力显微镜来量化的。所有16个显示单一调节系统的情况和6个观察到的具有两个调节系统的情况中的4个都被正确预测了。可调控模型参数的优化表明,局部和整体应力及其重要,他们共同决定了调节系统及其活动。此外,不同形变系统族的最佳临界分辨剪应力比值与文献中α-Ti一致。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117043
2. Solute enrichment induced dendritic fragmentation in directional solidification of nickel-based superalloys
镍基高温合金定向凝固中溶质富集诱发的枝晶碎裂
Neng Ren, Chinnapat Panwisawas, Jun Li✉, Mingxu Xia, Hongbiao Dong, Jianguo Li
Jun Li: li.jun@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117043
摘要
为了避免在单晶叶片中引入任意方向的新等轴晶粒(称为雀斑),应严格防止枝晶碎裂,因为单晶叶片的机制特性对晶界极为敏感。然而,高温合金铸件中雀斑的形成和分布机制仍有争议。本文通过为镍基单晶高温合金的开发并验证的细胞自动机-有限体积模型,揭示了定向凝固过程中热溶质对流、溶质偏析和枝晶组织之间的相互作用。模拟的通道分布、残余液体区域的形态、树枝状的尖端速度和雀斑晶粒与之前的实验观察结果吻合较好。本文直接预测了溶质富集诱导的枝晶断裂,即过度生长的枝晶树干中部被通道中过热的金属液熔化,枝晶顶部成为孤立的碎片。这些树枝状碎片而不是新成核的晶粒被证明是雀斑晶粒的根本原因。仿真结果也为研究操作参数对溶质分布和枝晶结构的影响提供了新的见解。定向凝固中不希望出现的横向热流促进了富含溶质的转移和通道的迁移,从而导致了枝晶的脱离。提高冷却速率对消除雀斑缺陷有明显的作用,因为较高的冷却速率促进了侧枝上三元枝晶臂的生长,并抑制了富含溶质的熔体向过度生长的枝晶的转移。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117017
3. Controlling martensitic transformation characteristics in defect-free NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated using laser powder bed fusion and a process optimization framework
利用激光粉末床熔合技术制造的无缺陷 NiTi形状记忆合金中的马氏体相变特征的控制及工艺优化框架
L. Xue, K.C. Atli, S. Picak, C. Zhang, A.Elwany, R.Arroyave, I. Karaman✉
I. Karaman: ikaraman@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117017
摘要
利用激光粉末床熔融技术(L-PBF)制造了完全致密的近等离子 (Ni50.1Ti49.9)和富含 (NiTiNi50.8Ti49.2)的形状记忆合金 (SMA)零件,其拉伸延展性高达16%,形状记忆应变为6%,拉伸超弹性高达4%。由于形成了小体积的 Ni4Ti3沉淀物,退火热处理略微改善了制造的富镍NiTi零件的超弹性。基于计算成本低廉的分析模型预测熔体池尺寸的工艺优化框架指导了生产全致密零件的最佳工艺参数的选择。该框架还包括验证模型预测的单轨实验,以及为防止形成缺乏融合的孔隙而允许的最大舱口间距标准。这个框架允许为目前的 NiTi SMA构建 L-PBF加工图,并显示在广泛的工艺参数范围内可以打印出完全致密的零件。通过控制 L-PBF工艺参数,特别是激光功率、激光扫描速度和体积能量密度,在导致完全致密部件的加工空间内,系统地证明了可以通过控制镍的蒸发来精确改变印刷部件的组成。通过参数选择的灵活性来打印无缺陷的 NiTi SMA,以及通过镍的优先蒸发来控制成分,为打印功能性的 NiTi SMA部件或设备提供了可能性,而无需进行后处理。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117012
4. Chemical short range order strengthening in BCC complex concentrated alloys
BCC复杂浓缩合金中的化学短程秩序强化
E. Antillon✉, C. Woodward, S.I. Rao, B. Akdim
E. Antillon: edwin.antillon@nrl.navy.mil
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117012
摘要
本文采用原子学方法对两种体心立方(BCC)的化学复杂合金(CCAs)进行退火,以评估化学短程秩序对合金强度的影响。这两种合金用简单的周氏原子间势分别表示为四元的Co16.67Fe36.67Ni16.67Ti30和三元的Nb33.33Ti33.33Zr33.33。使用蒙特卡洛方法在单个元素平均熔化温度的65%的温度下对化学随机单元进行退火,并使用分子动力学模拟估计初始和退火单元中移动 a/2[111]螺旋位错所需的临界应力。结果表明,退火热处理导致了 BCC四元合金相对于随机状态的软化,特别是对于在低温变形。另一方面,短程秩序对三元合金的固溶强化影响最小。这些结果是使用为 BCC化学复杂合金开发的替代性固溶体强化的 Suzuki模型的扩展来建模的。在本文中,该模型被修改以考虑到化学短程秩序的影响。模型结果和直接原子模拟数据之间显示出良好的一致性。所提出的模型在预测具有足够高温强度的 BCC CCA方面应该是有用的,这将加速用于航空航天的高温、高强度 BCC合金的开发。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 116973
5. Disordered interfaces enable high temperature thermal stability and strength in a nanocrystalline aluminum alloy
无序界面使纳米晶铝合金具有高温热稳定性和强度
Glenn H. Balbus, Johann Kappacher, David J. Sprouster, Fulin Wang, Jungho Shin, Yolita M.Eggeler, Timothy J.Rupert, Jason R.Trelewicz, DanielKiener, Verena Maier-Kiener, Daniel S. Gianola✉
Daniel S. Gianola: gianola@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116973
摘要
在能源经济中,结构材料的轻量化已被证明是不可或缺的,其前提是具有高强度-重量比的合金设计。现代铝合金在环境温度性能方面取得了长足的进步,并且适合于先进的制造途径,如增材制造,但在可以获得效率收益的高温下缺乏坚固性。本文我们展示了在界面上有意设计的无序性,这种概念通常与传统材料中的热失控有关,在偏析工程的三元纳米晶 Al-Ni-Ce合金中,表现出特殊的热稳定性和高温强度。原位透射电子显微镜与超速量热法和 X射线全散射法的结合表明, Ce和 Ni的协同共析推动了分离亚10nm富铝晶粒的无定形晶间膜的演变,从而产生了新的热稳定性。我们将这一有趣的行为归结为近乎平衡的界面条件,随后在封闭的无序区域内出现了动力学上迟缓的金属间析出。由此产生的高同源温度下的优异机械性能为合金设计和发现中促进无序的功效提供了证据。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117042
6. The role of β-Zr in a Zr-2.5Nb alloy during aqueous corrosion: A multi-technique study
β-Zr在 Zr-2.5Nb合金水腐蚀中的作用: 多技术研究
Junliang Liu✉, Guanze He✉, Anne Callow, Kexue Li, Katie L.Moore, HeidiNordin, MichaelMoody, SergioLozano-Perez, Chris R.M. Grovenor
Junliang Liu: junliang.liu@materials.ox.ac.uk
Guanze He: guanze.he@materials.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117042
摘要
Zr-2.5Nb合金被用作加拿大氘代铀( CANDU)核反应堆的压力管,并且其典型的起始显微结构包括横向和纵向拉长的 α-Zr晶粒和α-Zr晶粒之间的部分分解的β-Zr薄层。在这项研究中我们使用了最先进的显微镜技术来表征这种合金中长期热分解的β相以及在反应堆冷却剂回路中形成的氧化皮,目的是了解在使用温度下热分解行为的基础机制并探索分解的 β-Zr相在控制氧化锆的微观结构和微观化学中的作用,从而影响合金的一般耐腐蚀性。我们观察到这些 β-Zr层即使在制造周期结束时的 400℃短应力阶段后也会被严重分解,在α-Zr基体中形成紧密排列的 β-Nb沉淀物。我们已经证明这些带状物的氧化速度明显慢于周围的 α-Zr基体,而且每个带状物下都有氧化锆晶粒重新成核。我们的结论是正是由于热挤压和拉拔阶段产生的原始 β-Zr层的富含 Nb的残余物和这种新的致密氧化物的结合为氧化前沿提供了一个重要的障碍(也是对氢物种的渗透),所以原始制造过程中产生的特征分层微结构对于确定整体氧化行为非常重要。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117014
7. Natural and artificial ageing in aluminium alloys – the role of excess vacancies
铝合金的自然老化和人工老化--过剩空位的作用
Zi Yang, John Banhart✉
John Banhart: banhart@helmholtz-berlin.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117014
摘要
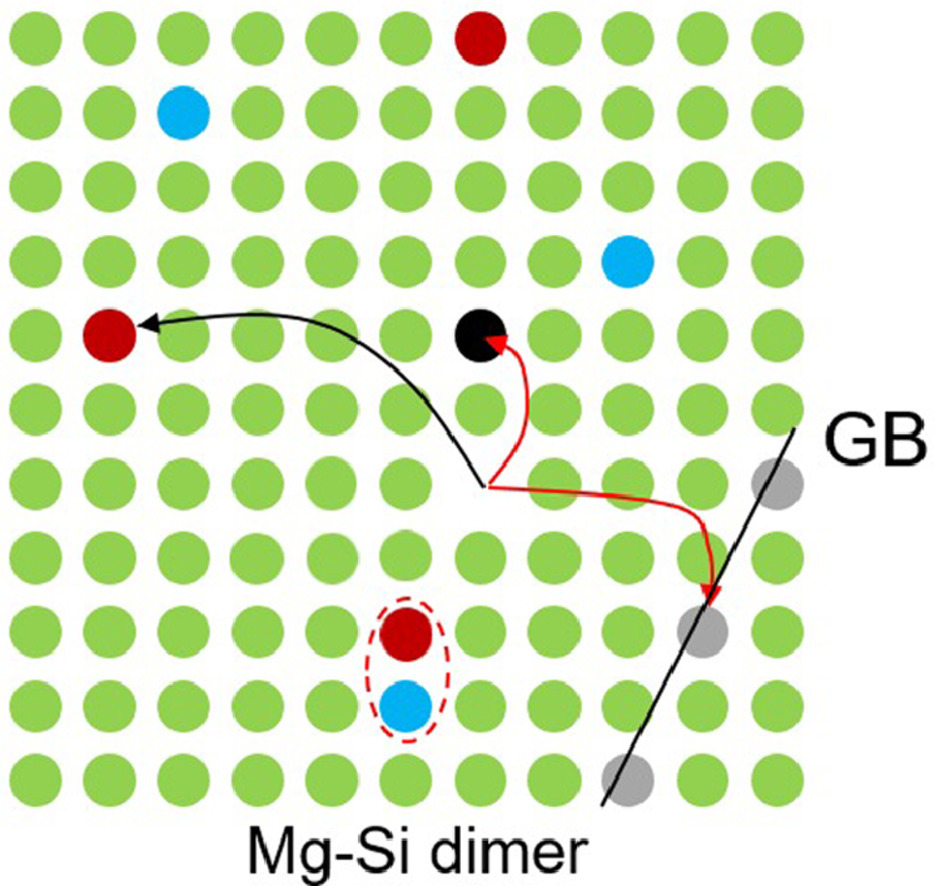
众所周知,在高温下对时效硬化铝合金进行固溶处理后,非平衡过剩空位被淬炼出来,在较低温度下的析出中发挥着重要作用。然而,对于在不同温度下对析出的贡献程度仍缺乏了解。在这项工作中,我们重新审视了这一经典问题,并通过硬度测量、差示扫描量热法和正电子湮灭寿命光谱法,研究了Al-Mg-Si合金中多余空位在自然和人工时效中的作用。然后我们应用了一个析出模型,涉及到基于第一性原理计算的参数的空位损失和溶质扩散的模拟。实验表明,在人工时效的最初几秒钟,多余的空位大部分被移除,几乎没有任何相应的硬化,也就是说,随后的硬化主要由平衡空位引发,与自然时效不同,自然时效主要由过量的空位驱动。我们重现了一个异常现象,即在较低的温度下,一定时间的硬化会更快,并通过空位湮灭和溶质扩散的不同激活能来解释这一点。在 Al-Mg-Si合金中显示的过量空位的作用在其他可时效硬化的合金中也可能是类似的,因此是一个普遍的现象。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117041
8. Anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard free energy and interfacial energies for binary alloys with pairwise interactions
具有成对相互作用的二元合金的各向异性卡恩-希利亚德自由能和界面能
P. Bellon✉, Q. Li
P. Bellon: bellon@illinois.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117041
摘要
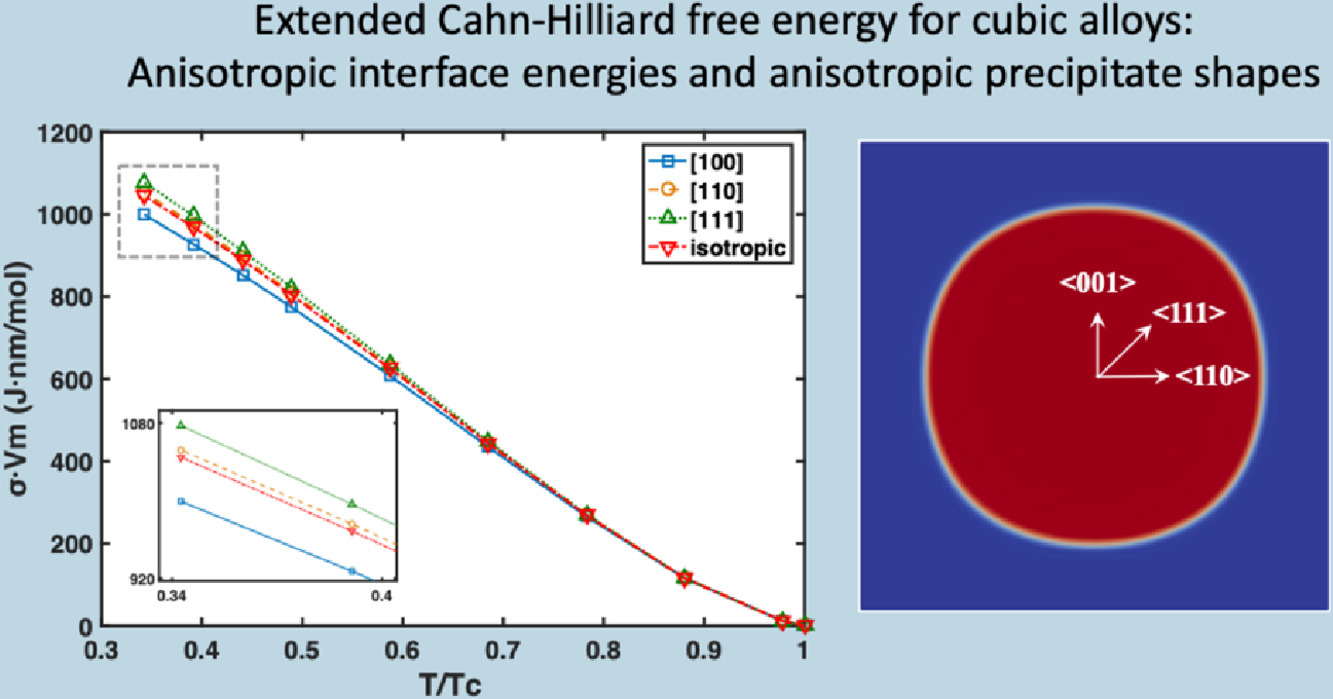
Cahn-Hilliard关于成分不均匀性对具有成对相互作用的二元合金自由能贡献的原始推导被扩展到包括高阶不均匀性项。对于立方晶格上的合金,第一个不均匀性的系数是一个二阶张量,并减少到一个标量,但它表明二阶和三阶不均匀性项是由四阶和六阶张量加权的,从而导致各向异性的贡献。此外,每个相互作用的壳都会产生一组独特的不均匀性系数,该系数由连接一个原子和该壳上的邻居的矢量集决定。这些系数是针对 FCC和 BCC合金与第四个最近的邻居之间的相互作用计算的。基于这些扩展的 Cahn-Hilliard自由能进行相场模拟,以测量沿特定结晶方向的界面自由能与温度的关系,并获得析出物的平衡形状。界面自由能以及由此产生的各向异性与离散模型和蒙特卡洛模拟得到的自由能进行了比较。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117023
9. Evaluating the grain-scale deformation behavior of a single-phase FCC high entropy alloy using synchrotron high energy diffraction microscopy
利用同步辐射高能衍射显微镜评估单相 FCC高熵合金的晶粒尺度变形行为
Hyun Seok Oh, Krista Biggs, Onur Güvenç, Hassan Ghassemi-Armaki, NarayanPottore, C. Cem Tasan✉
C. Cem Tasan: tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117023
摘要
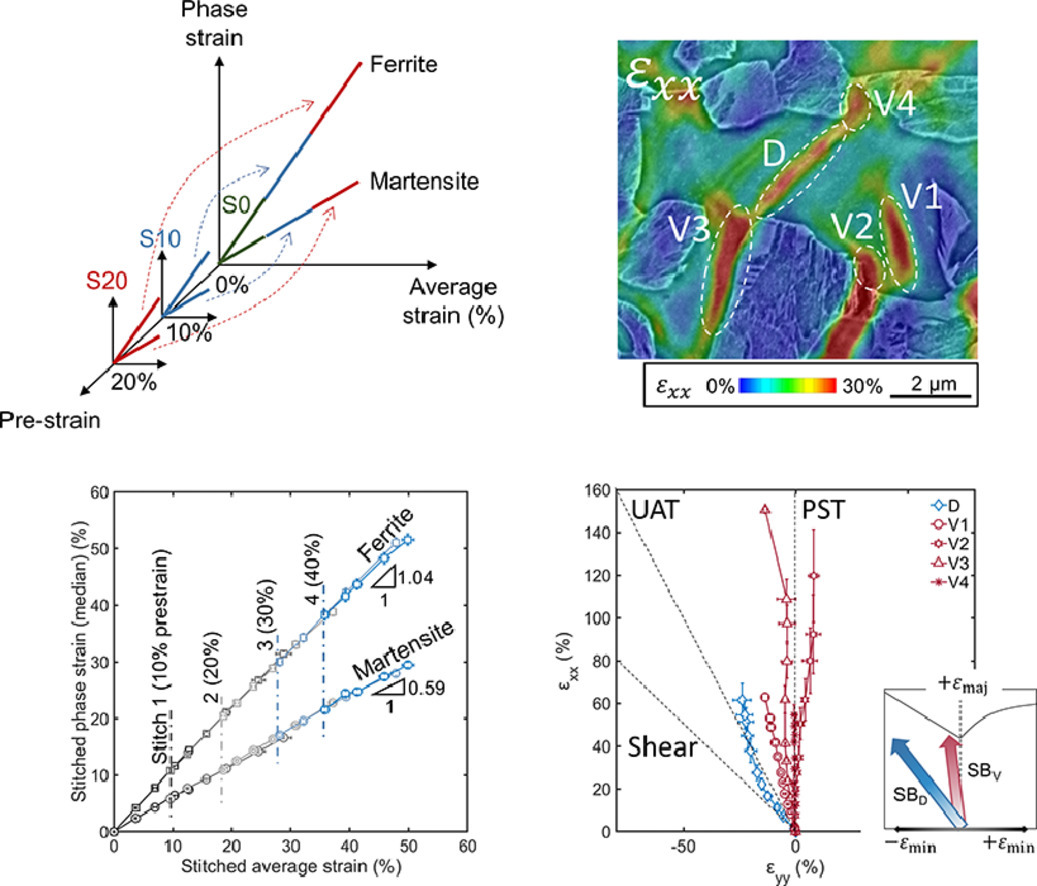
多相金属材料在塑性变形时表现出明显的应变分割和局部化水平。将这些微观结构过程与均匀变形的宏观极限(如塑性不稳定和断裂)联系起来,可以揭示抗破坏微观结构设计的准则。然而,这种联系由于缺乏来自高应变水平(接近或超过颈部)的应变划分和定位数据而受到阻碍。我们目前对多相材料塑性的理解的一个平行空白是关于微观尺度上应变路径发展的空间变化。显微数字图像关联是提供这种见解的最有力的实验方法,但由于晶体塑性或损伤引起的表面形貌演变,通常只限于低应变水平(<~15%)。因此在本文中,我们通过开发一种实用的方法来解决这些难题,该方法依赖于对预应变到不同水平的样品进行原位扫描电子显微镜(SEM)机械测试。并且将这种方法应用于双相钢,我们观察到铁素体和马氏体在整个变形过程中平均表现出线性应变分配趋势。然而,高度变形的铁素体区域(即前 4%最紧张的铁素体子集)在其容纳的应变水平上表现出指数级的增长,以及在不同的微观应变路径上的应变定位过程的顺序激活。马氏体成分在应变局部化过程和由此产生的微观应变路径中发挥了重要作用。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117024
10. An understanding of duplex microstructures encountered during high strength aluminium alloy laser beam melting processing
对高强度铝合金激光束熔炼加工过程中遇到的双相微结构的理解
Mathieu Opprecht✉, Jean-Paul Garandet✉, Guilhem Roux, Camille Flament
Mathieu Opprecht: mathieu.opprecht@cea.fr
Jean-Paul Garandet: jean-paul.garandet@cea.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117024
摘要
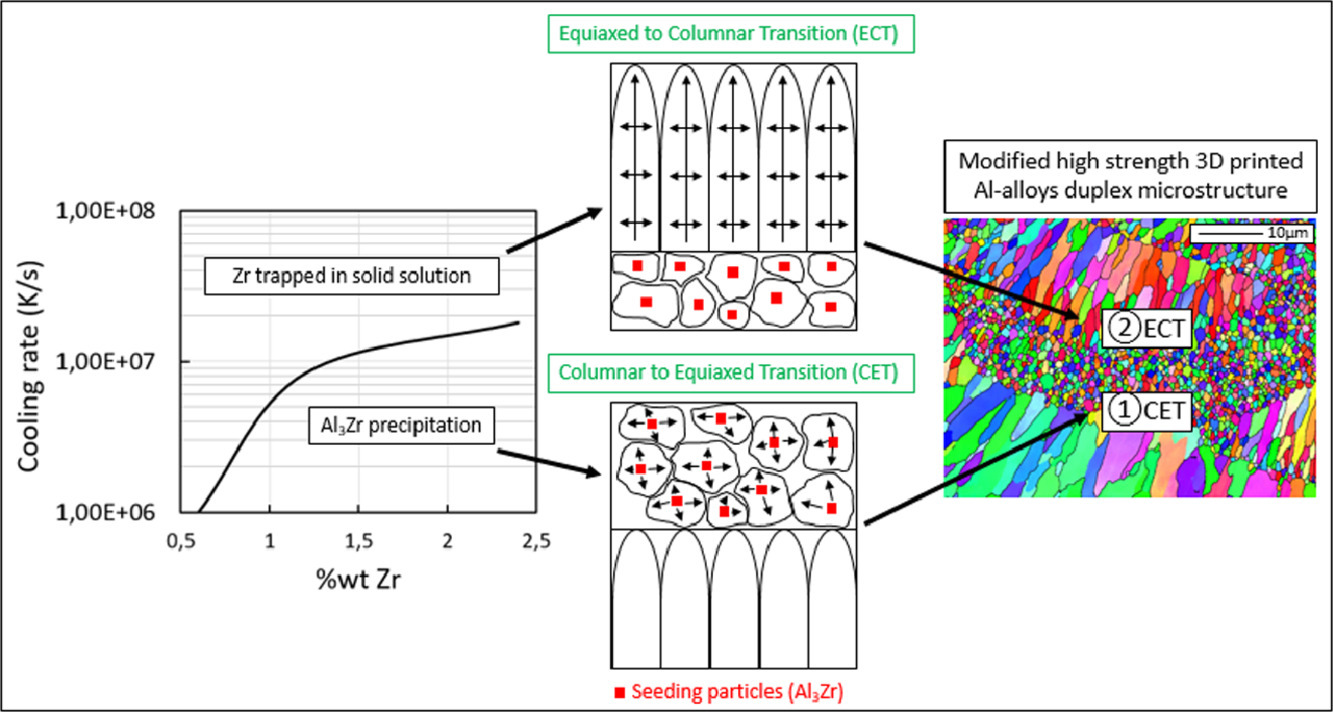
许多关于易热裂铝合金的激光束熔化(LBM)工艺的进展都集中在添加 Zr或 Sc元素上。 其目的是促进 Al3Zr或 Al3Sc析出,并为 α-Al相的形核提供理想的低能异质位点。双向晶粒的微观结构经常被诱导出来。在一个熔池内,凝固从底部开始,形成等轴结构。然后,在熔池中心周围的一个位置,会发现柱状生长的恢复。文献中公认的原因是形核密度随熔池深度的变化。本文的目的是利用标准形核理论以及进一步的实验数据来解释这种行为。为此,本文在 6061铝粉中加入了ZrO2和 Y2O3颗粒,以证实之前关于添加Yttria-Stabilized Zirconium的工作,即添加锆对6061 LBM加工的影响的假设。这些实验被认为是为理论形核框架提供了有用的信息。在适应的成核模型和成核点密度随遇到的热条件的变化之间发现了良好的相关性。防止 Al3Zr析出所需的临界冷却速率随着Zr浓度的增加而增加,并且这允许等轴带延伸。最后讨论了适应的模型参数的敏感性,使其适用性得到合理化。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117040
11. Graphene supported MgNi alloy nanocomposite as a room temperature hydrogen storage material – Experiments and theoretical insights
石墨烯负载的镁镍合金纳米复合材料作为室温储氢材料--实验和理论的见解
Sai Smruti Samantaray, P. Anees, Vinayan Bhaghavathi Parambath, Ramaprabhu S✉
Ramaprabhu S: ramp@iitm.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117040
摘要
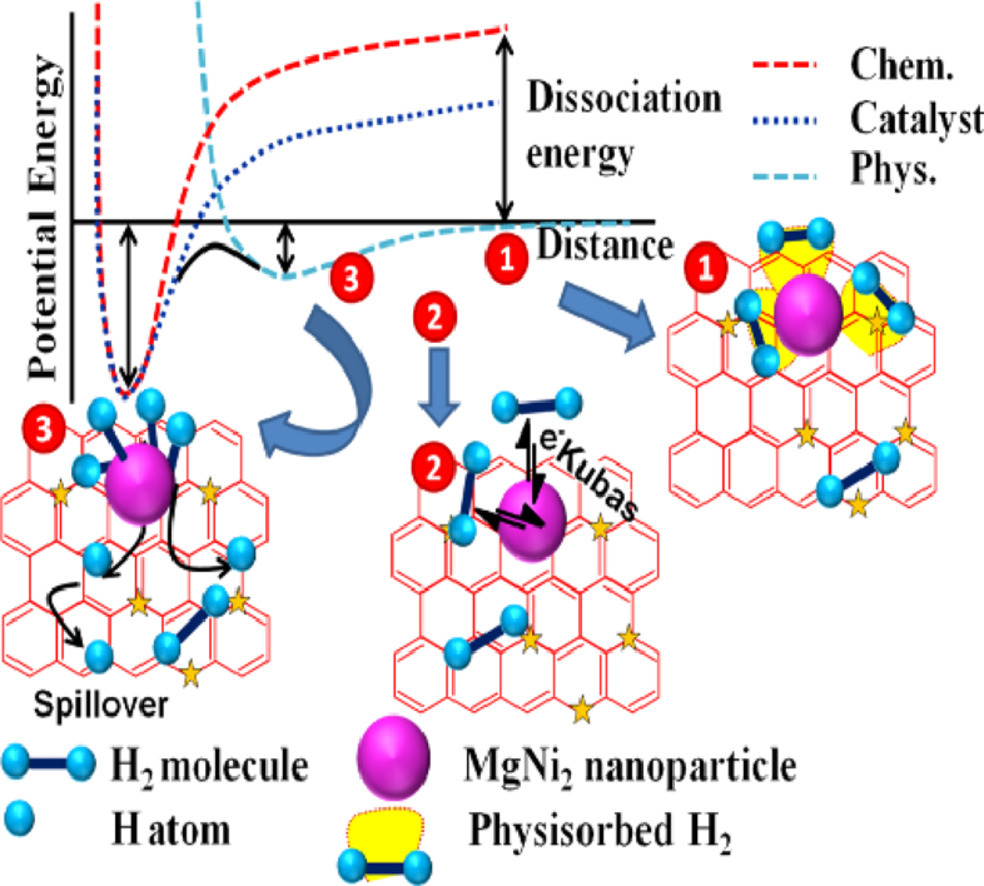
本文进行了实验研究与密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,去探测和了解石墨烯负载的 MgNi合金纳米复合材料的储氢特性。本文的主要亮点是发现了镁与镍的纳米结构和合金化及其在石墨烯MgNi/G)和氮 /硼掺杂的石墨烯( MgNi/NG MgNi/BG)上的分散导致了储氢能力的大幅提高。 在室温和 3MPa压力下测得的MgNi/G、 MgNi/BG和 MgNi/NG的储氢能力分别为 2.5%、 3.5%和 5.4%。值得注意的是,在相同的实验条件下,与 G(0.5%)、 BG (0.7%)和 NG (0.9%)的报告值相比,储氢能力的大幅提高。此外,DFT计算阐明了这种增强的吸氢能力所依据的吸附机制,并证实了实验结果。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117054
12. Spinodal Decomposition in Nanocrystalline Alloys
纳米晶合金中的亚稳分解现象
Xuyang Zhou, Reza Darvishi Kamachali✉, Brad L. Boyce, Blythe G. Clark, DierkRaabe, Gregory B. Thompson✉
Reza Darvishi Kamachali: reza.kamachali@bam.de
Gregory B. Thompson: gthompson@eng.ua.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117054
摘要
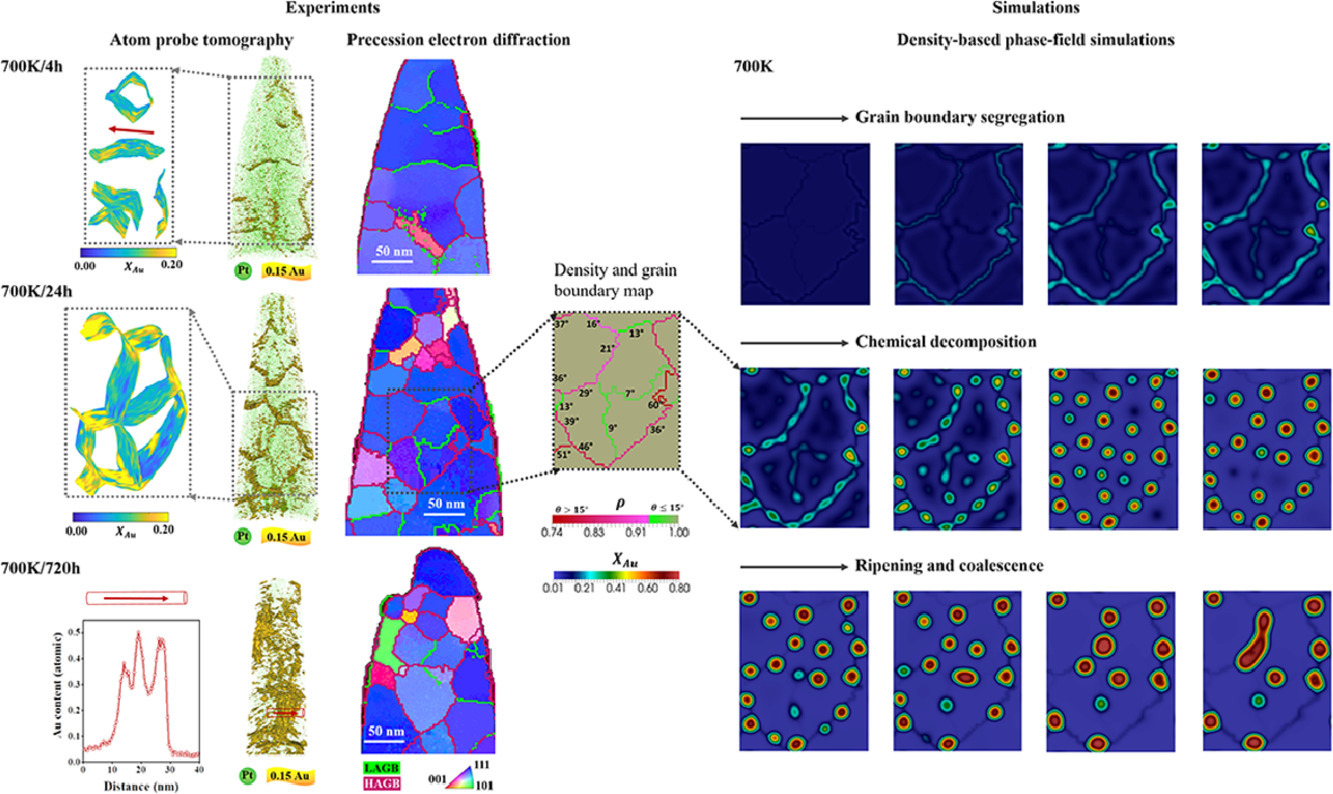
半个多世纪以来,在考虑合金中二次相的形成时,亚稳分解一直是一个关键现象。亚稳现象最突出的方面是其转化途径上缺乏能量障碍,为形核和生长机制提供了一个替代方案。对亚稳分解的经典描述往往忽略了缺陷(例如晶界)的影响,因为同类原子聚集的先天能力被假定为会引领这一过程。然而,在纳米晶合金中,有大量具有不同特征的晶界,结构上的异质性现象可以极大地影响化学分解行为。本文结合原子探针断层扫描、进动电子衍射和基于密度的相场模拟,探讨了晶界如何对Pt-Au纳米晶系统混溶间隙内的化学分解的时间演变。研究结果发现,晶界实际上可以有自己的混溶性间隙,极大地改变了纳米晶合金的亚稳分解。从竞争性的晶界偏析到无障碍的低维界面分解,多种界面状态的复杂领域都依赖于晶界特性。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117044
13. Influence of solidification structure on austenite to martensite transformation in additively manufactured hot-work tool steels
凝固结构对增材制造热作工具钢中奥氏体向马氏体转变的影响
Chia-Ying Chou, Niklas Holländer Pettersson, A. Durga, Fan Zhang, ChristosOikonomou, AnnikaBorgenstam, JoakimOdqvist, Greta Lindwall✉
Greta Lindwall: gretal@kth.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117044
摘要
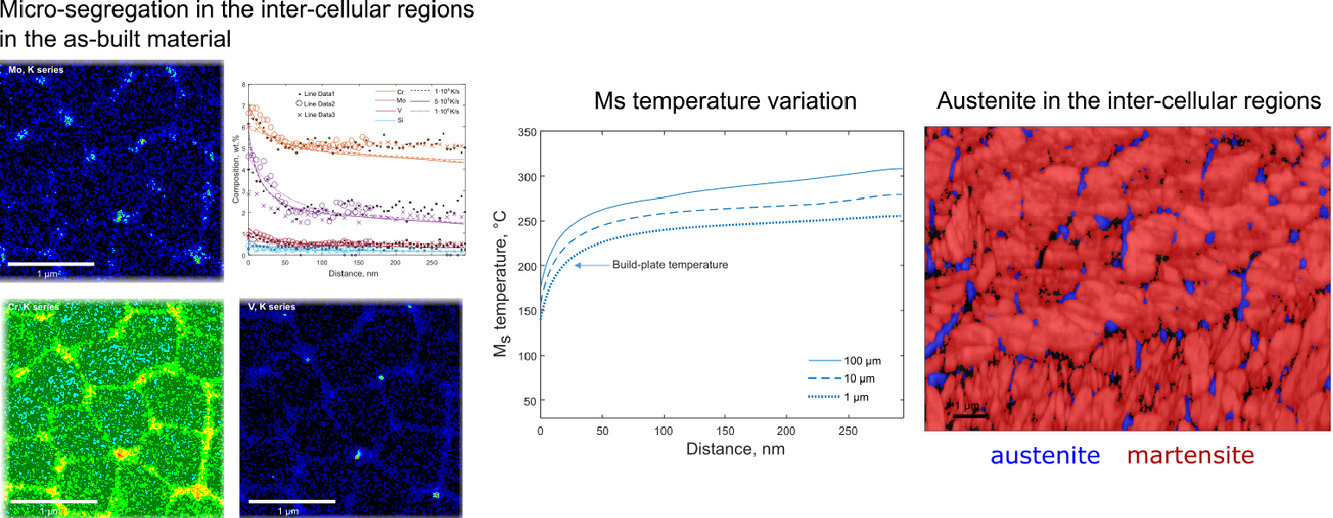
本文通过显微组织表征、计算热力学和动力学,详细研究了使用激光粉末床熔融技术(L-PBF)添加制造的热作工具钢的显微组织及其对后热处理的反应。在L-PBF过程中的高凝固速率和高冷却速率抑制了δ-铁素体的形成,取而代之的是直接含有晶胞亚结构的奥氏体相的凝固,其中合金元素已经偏析到晶胞间区域,凝固碳化物已经在晶胞交界处形成。然后部分奥氏体在较低温度下分解为马氏体。本文通过将复杂的凝固行为简化到一维扩散问题,可以预测微观的偏析,从而能够与纳米尺度上量化的测量偏析曲线进行详细的比较。沿着空间变化的成分进行的马氏体起始温度(Ms)计算表明,在观察到奥氏体的细胞间区域 Ms温度下降。建成后的微观结构中的奥氏体网络可以从 Ms温度与建板温度的成分依赖性和小尺寸奥氏体区域的机械稳定的综合影响中得到理解。这项工作通过预测钢对 L-PBF工艺和后热处理的反应,证明了基于计算热力学和动力学的计算工具在设计增材制造工具钢方面的能力。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117073
14. The nature of the maximum microhardness and thickness of the gradient layer in surface-strengthened Cu-Al alloys
表面强化的 Cu-Al合金中最大显微硬度的性质和梯度层的厚度的本质
C.X. Ren, Q. Wang✉, J.P. Hou, Z.J. Zhang, Z.F.Zhang✉, T.G. Langdon
Q. Wang: gmwang@imr.ac.cn(中国科学院金属研究所)
Z.F.Zhang: zhfzhang@imr.ac.cn(中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117073
摘要
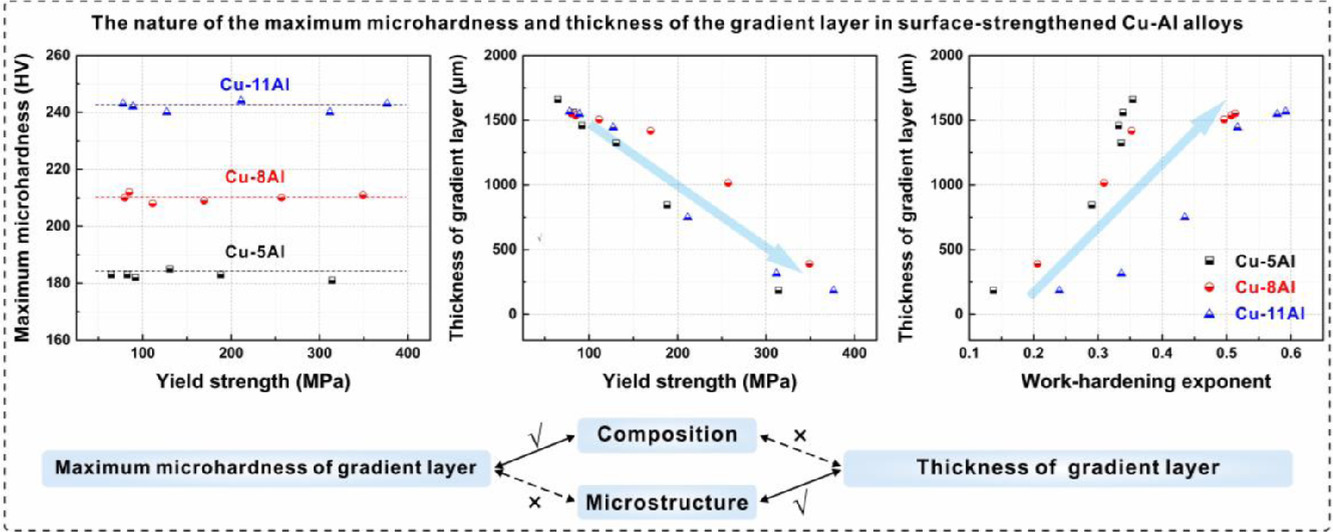
具有最大显微硬度和延伸厚度的梯度层的存在是极具吸引力的,因为它可以提高表面强化的金属材料的使用性能。本文通过表面旋压强化(3S)加工了不同铝含量和组织的铜铝合金,并研究了3S铜铝合金的梯度组织和显微硬度分布。实验结果表明,每组具有相同铝含量的 3S Cu-Al合金在最顶层的最大显微硬度大致相同,最大显微硬度随着铝含量的增加而增加。此外,3S Cu-Al合金中梯度层的厚度分别随着屈服强度的降低和加工硬化指数的增加而增加。本文还研究了最大显微硬度与决定杨氏模量和塑性变形方式的化学成分之间的关系,以及梯度层厚度与决定强度和加工硬化能力的组织之间的关系。研究发现,梯度层的最大显微硬度主要取决于化学成分;而梯度层的厚度主要取决于与强度和加工硬化能力,两者与组织密切相关。通过结合材料的成分设计和组织优化,提高表面强化强度,可获得最大显微硬度提高、厚度延长的表面强化材料梯度层。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117037
15. Slip localization in Inconel 718: A three-dimensional and statistical perspective
718合金中的滑移定位:三维和统计角度
M.A. Charpagne, J.M. Hestroffer✉, A.T. Polonsky, M.P. Echlin, D.Texier, V.Valle, I.J.Beyerlein, T.M.Pollock, J.C. Stinville
J.M. Hestroffer: mcharpagne@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117037
摘要
本文首次研究了多晶镍基高温合金Inconel 718在室温下单调拉伸载荷期间的滑移定位行为与三维微观结构的关系。多模式数据合并工具被用来在一个广泛的领域重新组合高分辨率数字图像相关(HR-DIC)数据和3D电子背散射衍射断层成像(3D EBSD)。这个过程能够重建三维微观结构中的滑移带平面。对 500个单独的滑移带进行的统计分析显示了它们的位置和特定的微观结构配置之间的强烈关联。特别是半数以上的滑移带来自三联结线(由三个晶体的交界处定义的三维线)。此外,最强烈和最长的滑移带位于靠近并平行于特定的退火孪晶界,并同时与三结线相连,而且滑移带在循环加载过程中成为关键的疲劳裂纹形核点。另外对实验微观结构进行晶体塑性有限元计算,以确定导致在这些特定微观结构区域形成高强度滑移带(局部塑性)或高晶格旋转区(非局部塑性)的滑动活动。


