金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.217,15 Sep. 2021
2021-12-18 来源:GS-Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文17篇,涵盖了高温合金、钛合金、形状记忆合金等,国内科研单位包括中科院沈阳金属所、上海交通大学、北京科技大学、清华大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 217 目录
1. Influence of microstructure on the application of Ni-Mn-In Heusler compounds for multicaloric cooling using magnetic field and uniaxial stress
微观组织对Ni-Mn-In Heusler复合材料磁场和单轴应力多热冷却应用的影响
2. Understanding imprint formation, plastic instabilities and hardness evolutions in FCC, BCC and HCP metal surfaces
了解FCC, BCC和HCP金属表面的压痕形成,塑性不稳定性和硬度变化
3. A unified description of mechanical and actuation fatigue crack growth in shape memory alloys
形状记忆合金中机械和驱动疲劳裂纹扩展的统一描述
4. Dynamics of Ga penetration in textured Al polycrystal revealed through multimodal three-dimensional analysis
通过多模态三维分析揭示了Ga在织构多晶铝中的渗透动力学
5. Removing basal-dissociated <c+a> dislocations by {10-12} deformation twinning in magnesium alloys
通过{10-12}变形孪晶去除镁合金中的基面离解的<c+a>位错
6. Bubble formation in helium-implanted nanostructured ferritic alloys at elevated temperatures
在高温下植入氦气的纳米结构铁素体合金中的气泡形成
7. Energy landscape modeling of crystal nucleation
晶体成核的能量景观建模
8. Theoretical investigation of the 70.5° mixed dislocations in body-centered cubic transition metals
体心立方过渡金属中70.5°混合位错的理论研究
9. An expansion of the Fisher model for concentration dependent grain boundary diffusion
浓度依赖晶界扩散的Fisher模型的扩展
10. Thermodynamic properties of the Yb-Sb system predicted from first-principles calculations
用第一性原理计算预测了Yb-Sb体系的热力学性质
11. Deformation mechanisms of Mg-Ca-Zn alloys studied by means of micropillar compression tests
采用微柱压缩试验研究Mg-Ca-Zn合金的变形机理
12. Stress-sensitive fatigue crack initiation mechanisms of coated titanium alloy
涂层钛合金应力敏感疲劳裂纹萌生机制研究
13. Revealing carbide precipitation effects and their mechanisms during quenching-partitioning-tempering of a high carbon steel: Experiments and Modeling
揭示高碳钢淬火-配分-回火过程中碳化物析出效应及其机理:实验与模拟
14. Insights into the selection mechanism of Widmanstätten growth by phase-field calculations
通过相场计算深入了解Widmanstätten生长的选择机制
15. Thermodynamics and design of nanocrystalline alloys using grain boundary segregation spectra
基于晶界偏析光谱的纳米晶合金热力学及设计
16. Multiphase field modeling of grain boundary migration mediated by emergent disconnections
由断裂介导的晶界迁移的多相场模拟
17. On the origin of mosaicity in directionally solidified Ni-base superalloys
定向凝固镍基高温合金镶嵌现象的起源
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117157
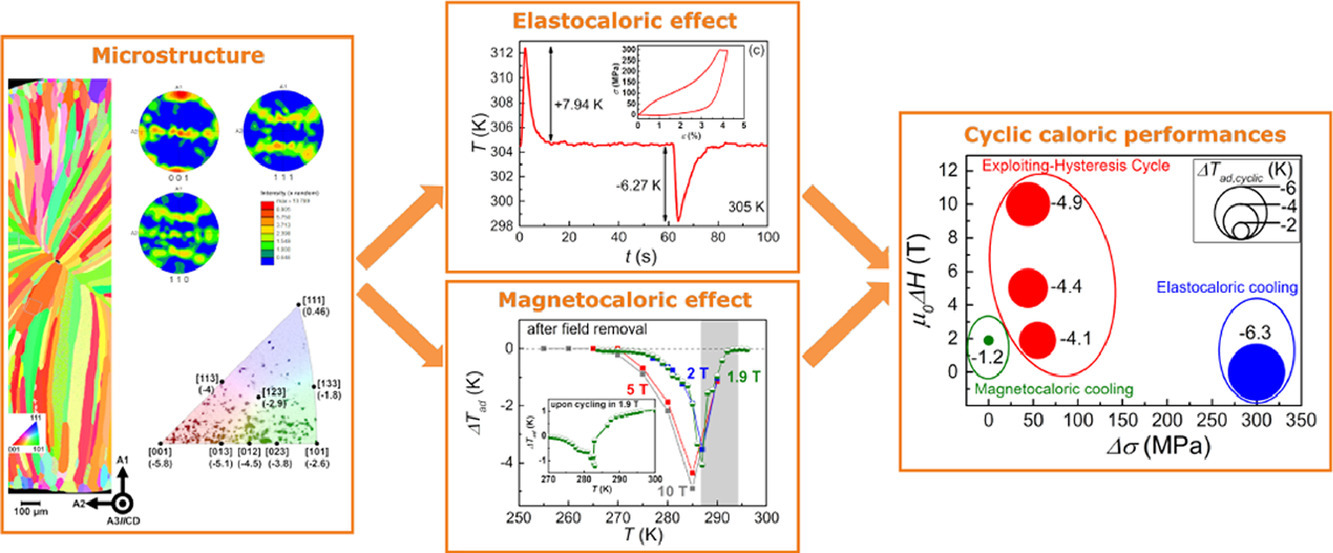
1. Influence of microstructure on the application of Ni-Mn-In Heusler compounds for multicaloric cooling using magnetic field and uniaxial stress
微观组织对Ni-Mn-In Heusler复合材料磁场和单轴应力多热冷却应用的影响
Lukas Pfeuffer✉, Adrià Gràcia-Condal, Tino Gottschall, David Koch, Tom Faske, Enrico Bruder, Jonas Lemke, Andreas Taubel, Semih Ener, Franziska Scheibel, Karsten Durst, Konstantin P.Skokov, Lluís Mañosa, Antoni Planes, Oliver Gutfleisch
Lukas Pfeuffer: lukas.pfeuffer@tu-darmstadt.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117157
摘要
利用镍锰基超磁性形状记忆合金对不同外部刺激(如磁场、单轴应力和静水压力)的巨大热响应的新型多热量冷却是一种有前途的节能和环保制冷的方法。然而,文献中很少讨论同时或连续施加几个外部场时微观组织的作用。本研究通过真空铸造和电弧熔炼合成了三元Ni-Mn-In合金,并分析了合金组织对磁场和单轴应力响应的影响。结合SEM-EBSD和应力-应变数据,揭示了织构对应力诱导的马氏体相变的显著影响。结果表明,<001>织构可以极大的降低临界转变应力。进一步研究了晶粒尺寸对材料失效的影响,以及它对磁场诱导相变动力学的影响。此外,本研究还建立了温度-应力和温度-磁场相图,并以ΔsT和ΔTad表征了单片热工性能。而且循环的ΔTad值与在多热量利用-磁滞循环中取得的值进行了比较。事实证明,真空铸造组织和两种刺激的结合能够在适度的外部场中实现出色的热量效应,且显著地超过了单一的热效应。特别是对于Ni-Mn-In来说,当施加55MPa的中等连续应力时,在 1.9T的磁场中的最大循环效应增加了200%以上,达到-4.1K。研究结果表明了微观组织对于Ni-Mn基超磁性形状记忆合金的多热冷却具有关键的作用。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117122
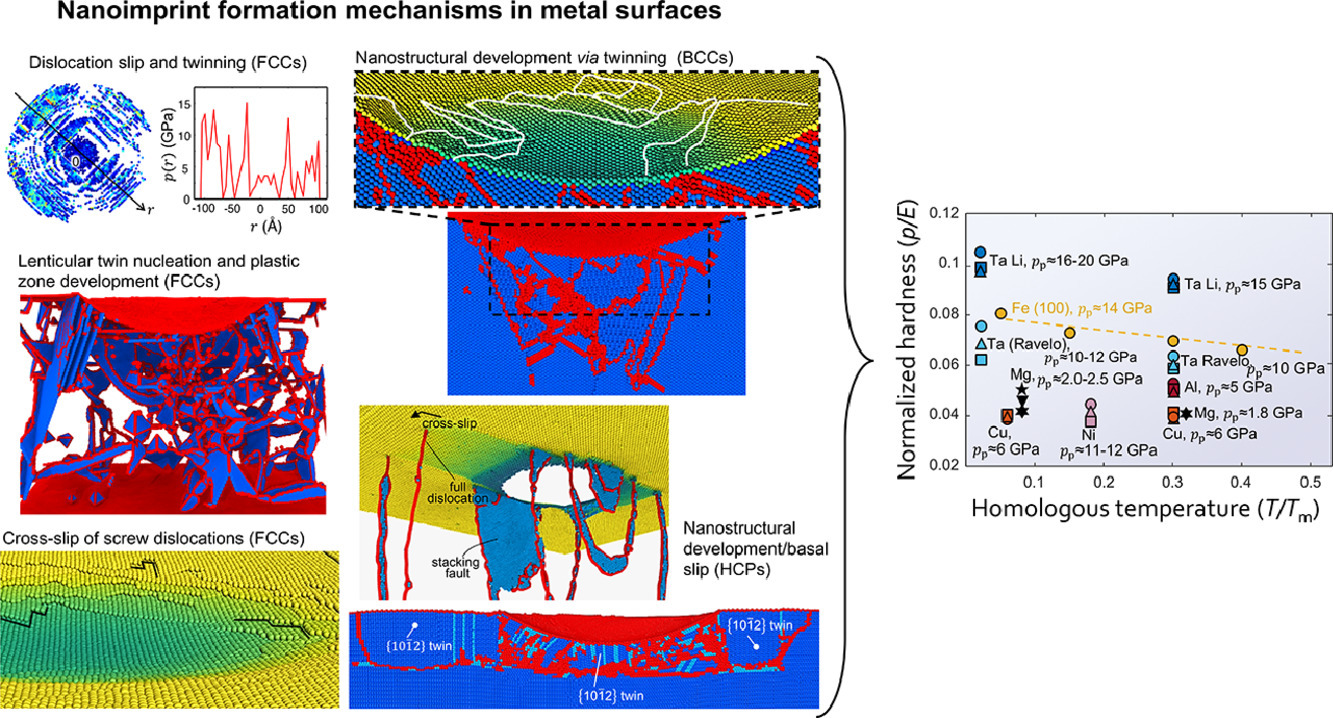
2. Understanding imprint formation, plastic instabilities and hardness evolutions in FCC, BCC and HCP metal surfaces
了解FCC, BCC和HCP金属表面的压痕形成,塑性不稳定性和硬度变化
Javier Varillas, Jan Očenášek, Jordi Torner, Jorge Alcalá
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117122
摘要
金属表面的纳米压痕实验的特点是随着永久纳米压痕和致密缺陷网络的发展,纳米压痕实验开始出现塑性不稳定性。本论文使用实际尺寸的钝化(球形)尖端对FCC、BCC和HCP金属的纳米压痕实验进行大量的分子动力学模拟,并将结果与实验测量进行详细比较。研究结果表明了缺陷过程决定了接触塑性变形阻力,具有突然塑性不稳定性的过渡阶段的发展以及以恒定位错密度(ρp)处硬度(pp)趋于平稳为特征的自相似稳态的演变过程。永久纳米压痕的发生受堆垛层错和纳米孪晶、整个压痕过程中纳米结构区域和微晶的堆积、表面螺旋位错的交叉滑移和交叉扭结以及塑性区内缺陷再活动事件的发生所制约。由于这些机制,硬度 (pp)和杨氏模量(E)之间的比值在BCC的Ta 和Fe中变得更高,其次是FCC 的Al、HCP的Mg 和大层错宽度的FCC的Ni和Cu。最后,当纳米压痕的形成与缩进的微小材料体积的单轴响应相关时,硬度与屈服强度之比(pp /σys)从7 变化到10,这在很大程度上超过了连续塑性的界限(2.8)。本研究的结果对理解压痕尺寸效应具有普遍意义,其中极端纳米级硬度值的出现与大应变梯度下独特的压痕形成过程的发生有关。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117155
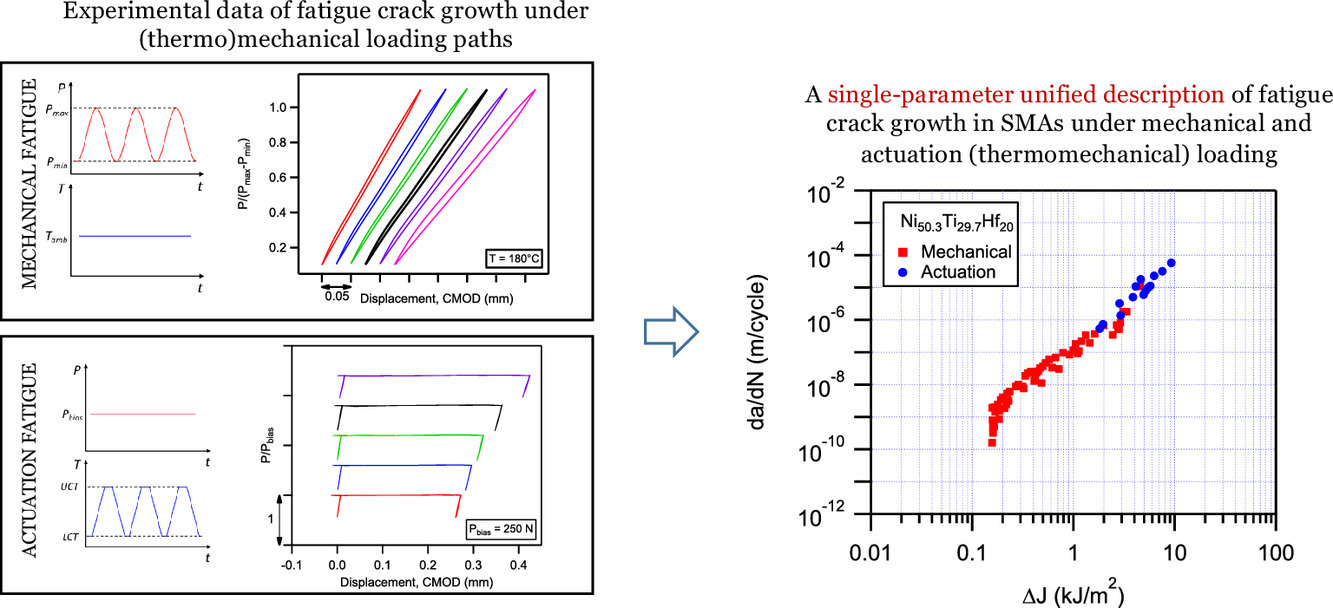
3. A unified description of mechanical and actuation fatigue crack growth in shape memory alloys
形状记忆合金中机械和驱动疲劳裂纹扩展的统一描述
Behrouz Haghgouyan, Benjamin Young, Sezer Picak, Theocharis Baxevanis✉, Ibrahim Karaman, Dimitris C.Lagoudas
Theocharis Baxevanis: tbaxevanis@uh.edu; tbaxevanis@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117155
摘要
疲劳损伤容限方法依靠断裂力学概念来明确说明疲劳裂纹的扩展过程。这些方法通常采用Paris方程,该方程通过实验校准的参数,将每周期的裂纹增长与循环加载期间的应力强度系数ΔK的变化范围联系起来。对近裂纹尖端应力和应变场的单一参数描述的有效性条件限制了ΔK对形状记忆合金(SMA)在一般热机械加载路径下的抗疲劳裂纹增长的适用性。这些条件对于循环ΔJ积分方法来说是非常宽松的,它可以在更广泛的加载条件和几何配置中实现相似。因此,ΔJ可以作为SMAs中抗热机械疲劳裂纹扩展的潜在统一描述符,这一论断在本论文中对来自高温SMA Ni50.3Ti29.7Hf20的纯机械和驱动疲劳裂纹扩展实验的数据进行了验证。在后者中,紧凑的拉伸试样在恒定的负载下,在允许稳定相在每个循环中交替的上限和下限循环温度之间进行热循环。结果表明,基于ΔJ积分的Paris型幂律裂纹扩展表达式可以用一组单一参数来拟合这两类实验的疲劳裂纹增长速率数据。这种针对驱动和机械疲劳裂纹扩展速率的新分析方法为SMAs中的疲劳裂纹扩展提供了一个统一的描述,并且可以从更容易检测的机械疲劳裂纹扩展速率来估计出测量起来很费力且具有挑战性驱动疲劳裂纹扩展速率。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117145
4. Dynamics of Ga penetration in textured Al polycrystal revealed through multimodal three-dimensional analysis
通过多模态三维分析揭示了Ga在织构多晶铝中的渗透动力学
N. Lu, S. Moniri, M.R. Wiltse, J. Spielman, N. Senabulya, A.J. Shahani✉
A.J.Shahani: shahani@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117145
摘要
本研究对液态 Ga 在温度为31.9°C的多晶体Al棒中的渗透进行了原位研究。基于实验室的新型多模态X射线成像平台的帮助下,使我们能够描述三维(3D)晶粒结构、Ga的润湿行为以及两者之间的关联性。与随机分布相比,样品沿着[001]方向显示出强烈的织构以及更高比例的低角度晶界(LAGBs),这表明高角度晶界(HAGBs)的连通性较差。在接触液态金属1小时后检测到沿HAGBs的Ga通道,但这种通道在长时间退火后逐渐消失。本研究进一步从几何渗透理论和扩散理论的角度来解释这一现象,这些理论指出了有限HAGB连通性和增强的通过位错管从HAGB渗漏到体外的Ga扩散的协同效应。本研究提供了关于织构和晶界连通性对液态金属脆化动力学的影响的详细见解,与具有高层错能的抗脆性材料的晶界工程有关。
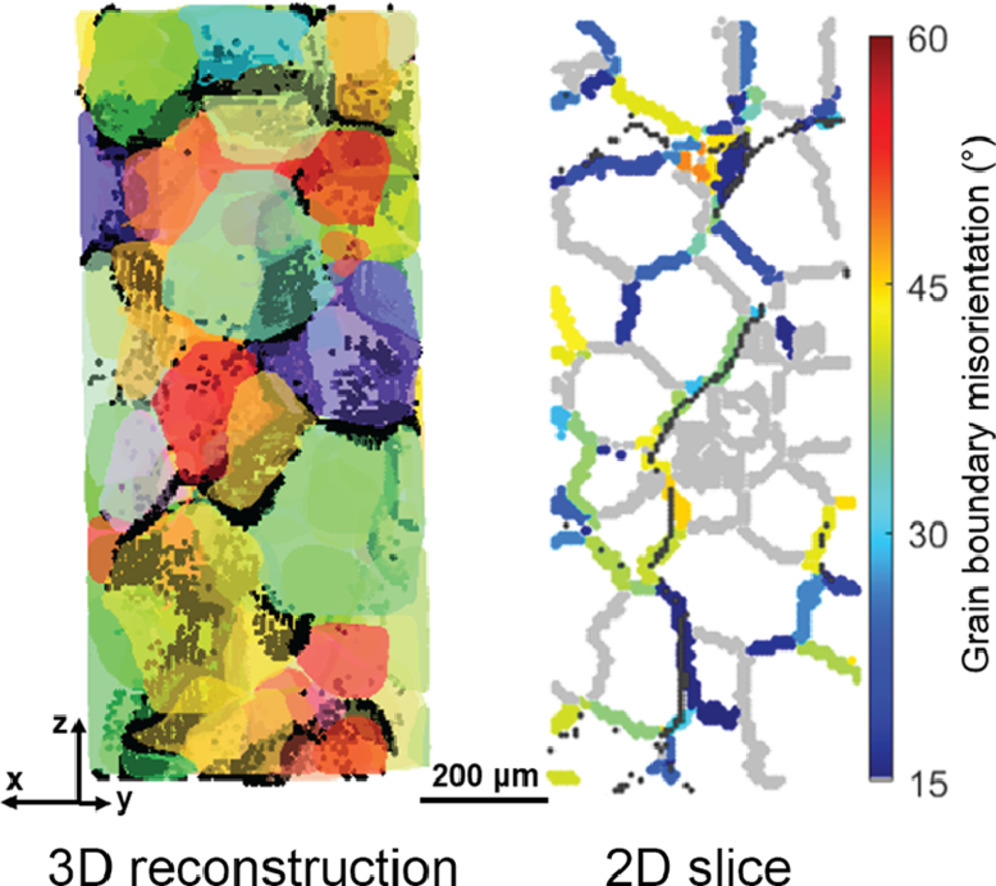
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117170
5. Removing basal-dissociated <c+a> dislocations by {10-12} deformation twinning in magnesium alloys
通过{10-12}变形孪晶去除镁合金中的基面离解的<c+a>位错
Xinzhe Zhou, Huhu Su, Hengqiang Ye, Zhiqing Yang✉
Zhiqing Yang: yangzq@imr.ac.cn; yangzq34@yahoo.com, 中科院沈阳金属所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117170
摘要
基于原子分辨率观察、界面缺陷理论和分子动力学(MD)模拟,研究了循环变形的 Mg 合金中{10-12}孪晶界(TBs)与位错的反应。原子分辨率观察提供了{10-12}孪晶界分别与基面<a60>、基面解离的<c+a>位错以及孪晶界的四次迁移发生反应的证据。MD模拟结果表明, Mg中固定的基面解离的<c+as>, <c+a60> 和<c>位错可以被纳入{10-12}孪晶界中去产生台阶。并且在低剪应力的作用下,台阶可以与孪晶和去孪晶时的孪晶界一起移动。而且这种台阶在同时施加剪切应力和法向应力的情况下通常可以产生<a60>位错。重要的是,在{10-12} 变形孪晶中,将固定的基面解离的<c+a>位错转变为滑动的<a60>位错所需的法向应力要远低于将基面<a60>位错转变为<c+a>位错所需的法向应力。本研究的结果可能对全面了解变形孪晶、<c+a>位错以及它们在镁合金塑性变形中的相互作用/反应有重要意义。

ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117165
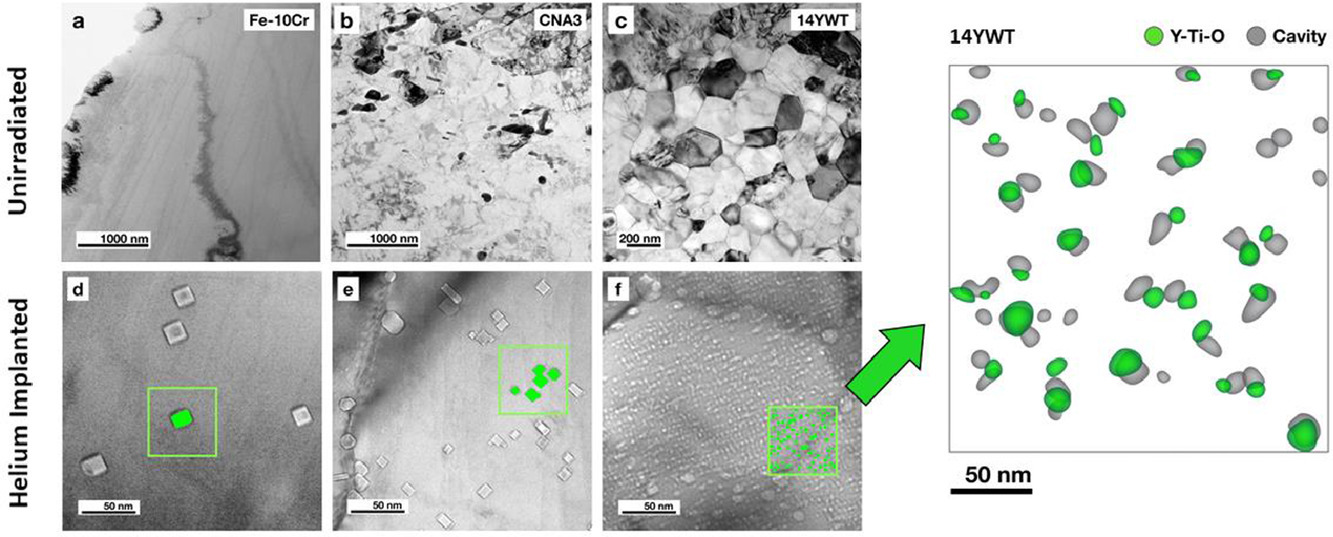
6. Bubble formation in helium-implanted nanostructured ferritic alloys at elevated temperatures
在高温下植入氦气的纳米结构铁素体合金中的气泡形成
Yan-Ru Lin✉, Wei-Ying Chen, Lizhen Tan, David T.Hoelzer, Zhanfeng Yan, Cheng-Yu Hsieh, Chun-Wei Huang, Steven John Zinkle
Yan-Ru Lin: ylin52@vols.utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117165
摘要
通过扫描/透射电子显微镜(S/TEM)对Fe-9/10Cr二元合金和两种弥散强化纳米结构合金(CNA3和14YWT,分别含有直径为5-10nm 的碳化物和氧化物颗粒)在500到900℃ 下原位和非原位植入约10000 appm 后的氦气后氦气气泡的形成进行了研究。高分辨率STEM 图像和电子能量损失光谱(EELS)的结合结果显示14YWT中的Y-Ti-O纳米颗粒是均匀分布的,并表现出气泡附着在纳米团簇上的一对一的关系。在900℃的原位实验中,Fe-10Cr 模型合金的晶界开裂很严重,但在纳米结构合金中没有发现。从500到900°C的范围内,气泡大小一般随着辐照温度的增加而增加,而气泡密度随着温度的增加而减少。在相同的温度下,注入材料中的气泡大小依次为Fe-9/10Cr > CNA3 > 14YWT,而气泡密度则呈现相反的顺序。观察到的纳米结构合金的气泡数密度与纳米颗粒密度相当,表明这两种合金中的纳米颗粒都能有效地捕获氦元素。研究结果表明,在纳米结构合金中可以通过将氦气封存到较小的气泡中(这导致较低的体积膨胀值)来控制非常高的氦气浓度,并将氦气从晶界中屏蔽。这可以归因于与纳米团簇相关的更高的吸收强度或不同类型的纳米团簇之间的氦捕获能力。

ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117163
7. Energy landscape modeling of crystal nucleation
晶体成核的能量景观建模
Collin J. Wilkinson, Daniel R. Cassar, Anthony V. DeCeanne, Katelyn A. Kirchner, Matthew E. McKenzie, Edgar D. Zanotto, John C. Mauro✉
John C. Mauro: jcm426@psu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117163
摘要
成核是所有材料科学中一个关键的相变过程。在晶体成核方面,对成核率的准确认识对于设计下一代玻璃陶瓷和其他复合材料至关重要;然而,晶体成核率随温度的定量预测仍然难以实现。这项工作提出了一种能量景观方法来说明成核的热力学和动力学。这种能量景观方法与作为模型的二硅酸钡系统的实验成核数据显示出相当的一致性。它还被用来深入了解经典 成核理论(CNT)的基本物理学和计算成核率的新方法。
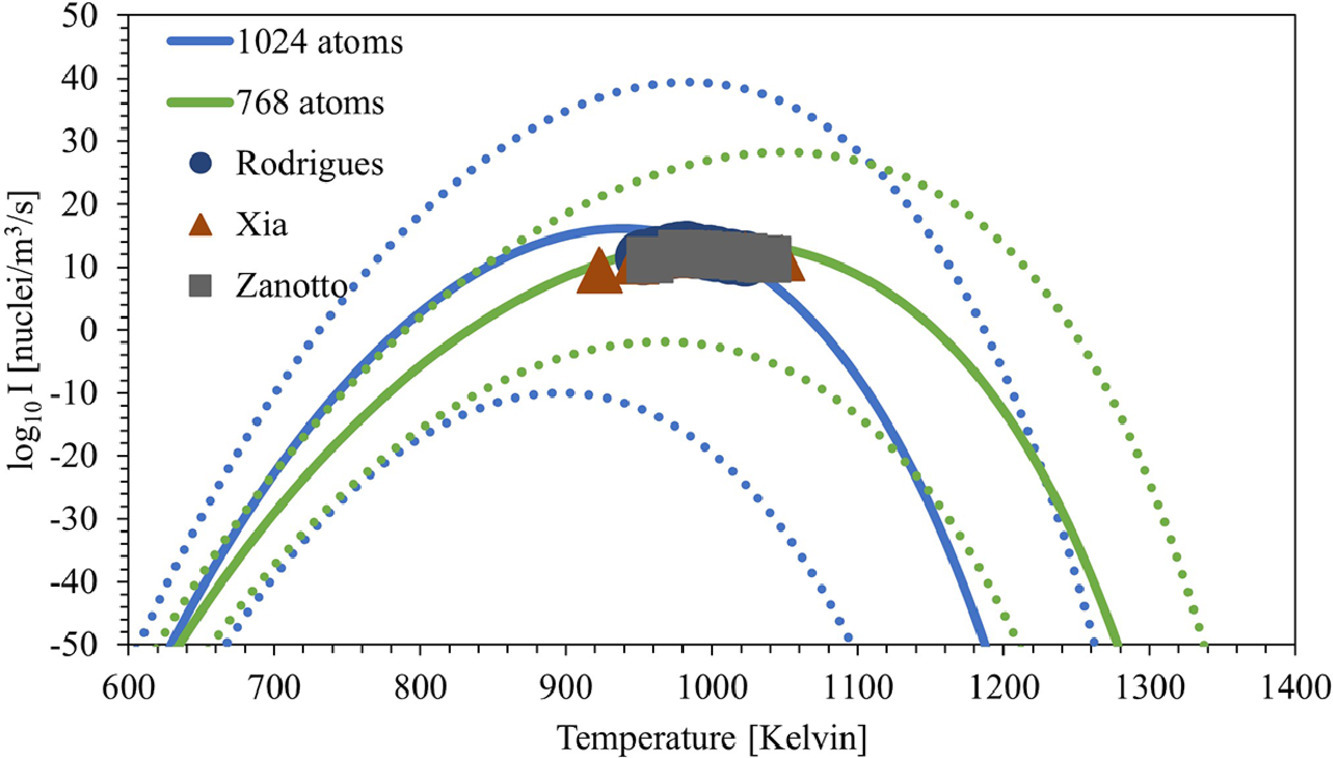
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117154
8. Theoretical investigation of the 70.5° mixed dislocations in body-centered cubic transition metals
体心立方过渡金属中70.5°混合位错的理论研究
Lorenz Romaner✉, Tapaswani Pradhan, Anastasiia Kholtobina, Ralf Drautz, Matous Mrovec
Lorenz Romaner: lorenz.romaner@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117154
摘要
体心立方(bcc)金属的低温塑性受12 <111>螺旋位错的控制,因为它们的核心是紧凑的、非平面的。有人提出70.5°混合(M111)位错也可能表现出特殊的核心结构和相当大的 Peierls 应力,但理论和实验证据仍然不完整。在本研究中,在原子模拟的基础上对五种bcc过渡金属中的M111位错进行了详细的比较研究。采用密度泛函理论和半经验的原子间势来研究M111位错的核心结构和 Peierls 势垒。计算结果表明,对M111特性的可靠预测不仅对原子间势的可靠性提出了非常严格的考验,而且对第一原理计算也是一种挑战,需要进行仔细的收敛研究。研究显示,不同的bcc过渡金属的Peierls势垒和应力有很大的不同。W 和Mo有相当大的势垒,而Nb、Ta和Fe的势垒则相当小。本研究的预测结果与内摩擦测量结果一致,并提供了对bcc金属塑性的新见解。
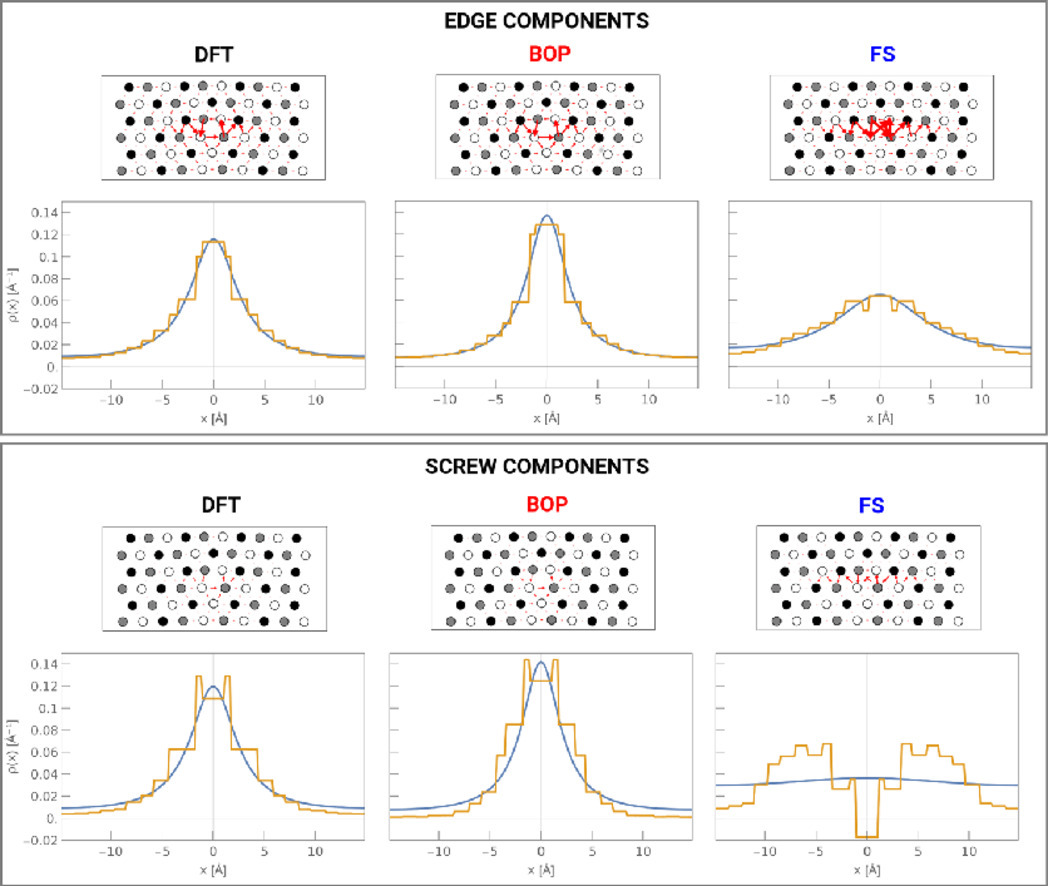
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117056
9. An expansion of the Fisher model for concentration dependent grain boundary diffusion
浓度依赖晶界扩散的Fisher模型的扩展
M. Short, K. Woll✉
K. Woll: karsten.woll@kit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117056
摘要
在考虑浓度相关的晶界扩散时,在Fisher 模型的边界条件中衍生出一个额外的项,用于在低扩散剂浓度条件下快速扩散边界的原子传输,从而形成了一个扩展模型。使用隐式有限差分模型对其有效性进行了评估,该模型表明最小和最大晶界扩散值之间至少要有0.5到0.6 个数量级的差异才能观察到显著的影响。本研究也对晶界扩散系数随浓度的增加或减少的情况进行了研究。虽然对测量的晶界扩散系数的影响可以忽略不计,但晶界扩散的浓度依赖性大大影响了晶界周围的元素分布。后者直接影响纳米晶材料中晶粒长大或相变等与晶界有关的冶金现象。
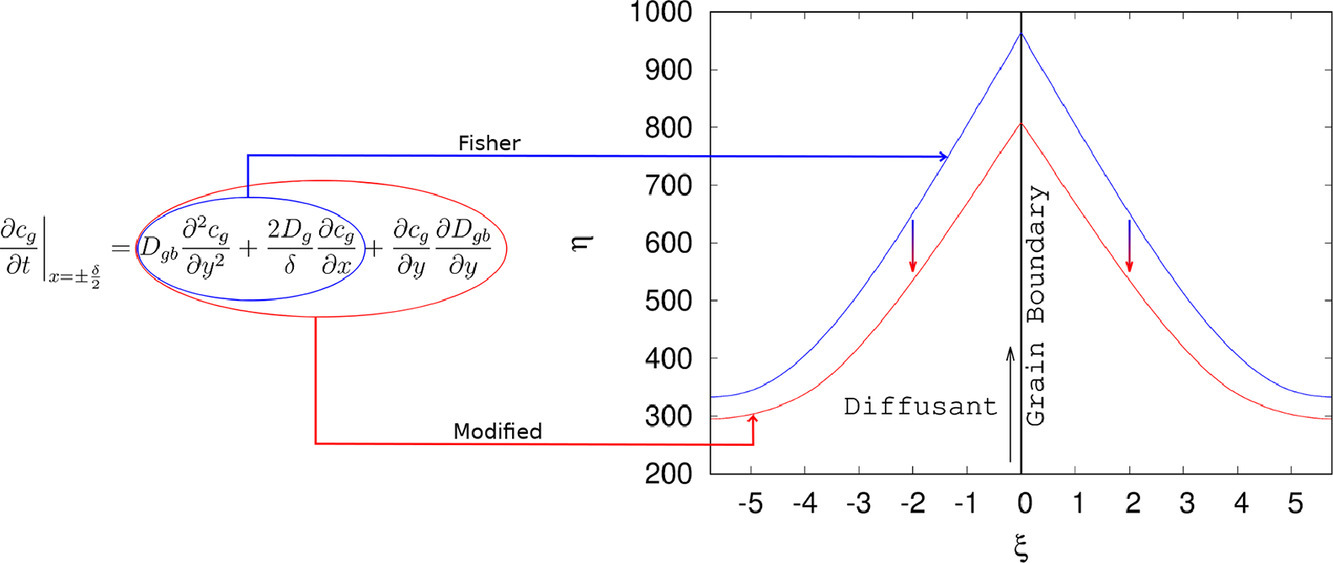
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117169
10. Thermodynamic properties of the Yb-Sb system predicted from first-principles calculations
用第一性原理计算预测了Yb-Sb体系的热力学性质
XiaoYu Chong✉, Jorge Paz Soldan Palma, Yi Wang, Shun-Li Shang, Fivos Drymiotis, Vilupanur A. Ravi, Kurt E. Star, Jean-Pierre Fleurial, Zi-Kui Liu
XiaoYu Chong: chongxiaoyu007@163.com, 昆明理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117169
摘要
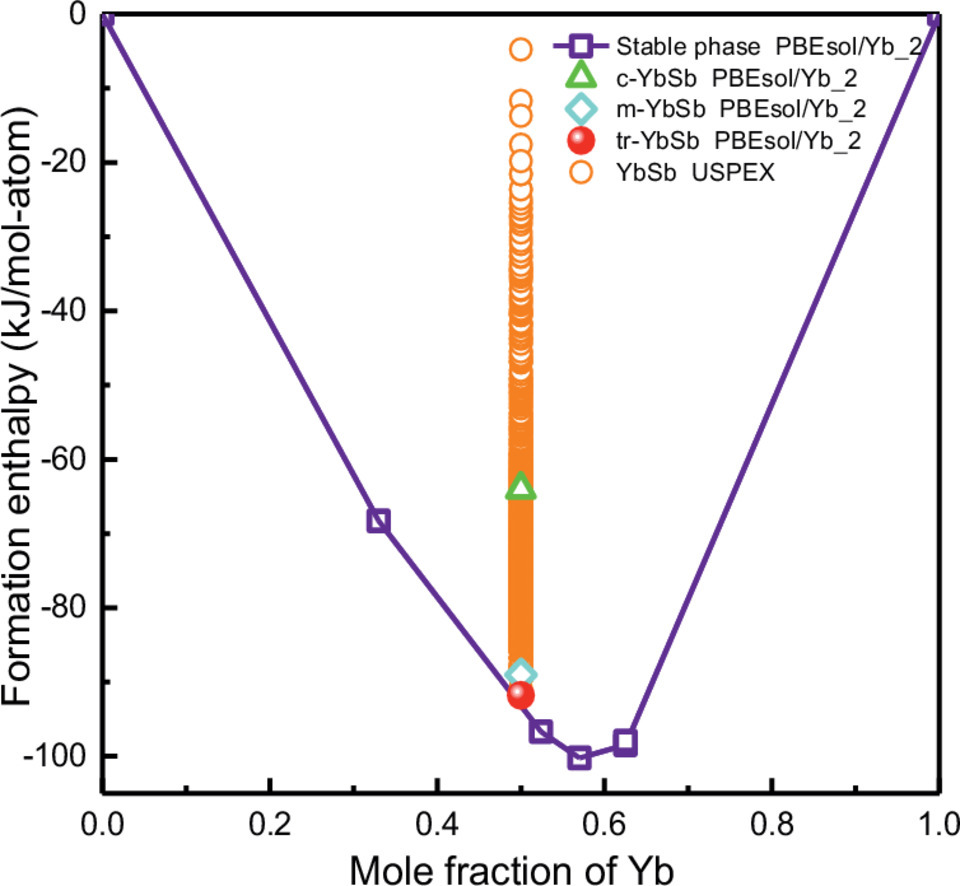
本研究通过基于第一性原理的准谐波声子方法研究了Yb-Sb 系统的热力学特性,得到了随温度变化的等压热容、熵、生成焓、等温体模量和热膨胀。研究了使用不同的交换相关函数和赝势对热力学性质的影响。结果显示,结合Perdew-Burker-Ernzerhof 固体泛函修正法(PBEsol)和所有f电子冻结在核内的赝势是最佳选择。这种组合导致了对相对相稳定性和热力学性质的总体良好的描述,但岩盐YbSb化合物除外,该化合物在凸壳以上的能量为25 kJ/mol-atom。这种差异可能是由于岩盐YbSb结构和其他Yb-Sb化合物之间的Yb价态发生了变化。此外,目前的计算结果表明,Yb16Sb11化合物是稳定的。对拉伸力常数的分析表明,极强的Yb-Sb 键是Yb11Sb10、Yb16Sb11、h-Yb5Sb3和Yb4Sb3在高温下稳定的原因。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117151
11. Deformation mechanisms of Mg-Ca-Zn alloys studied by means of micropillar compression tests
采用微柱压缩试验研究Mg-Ca-Zn合金的变形机理
Jingya Wang, Yiwen Chen, Zhe Chen, Javier Llorca✉, Xiaoqin Zeng✉
Javier Llorca: javier.llorca@imdea.org
Xiaoqin Zeng: xqzeng@sjtu.edu.cn, 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117151
摘要
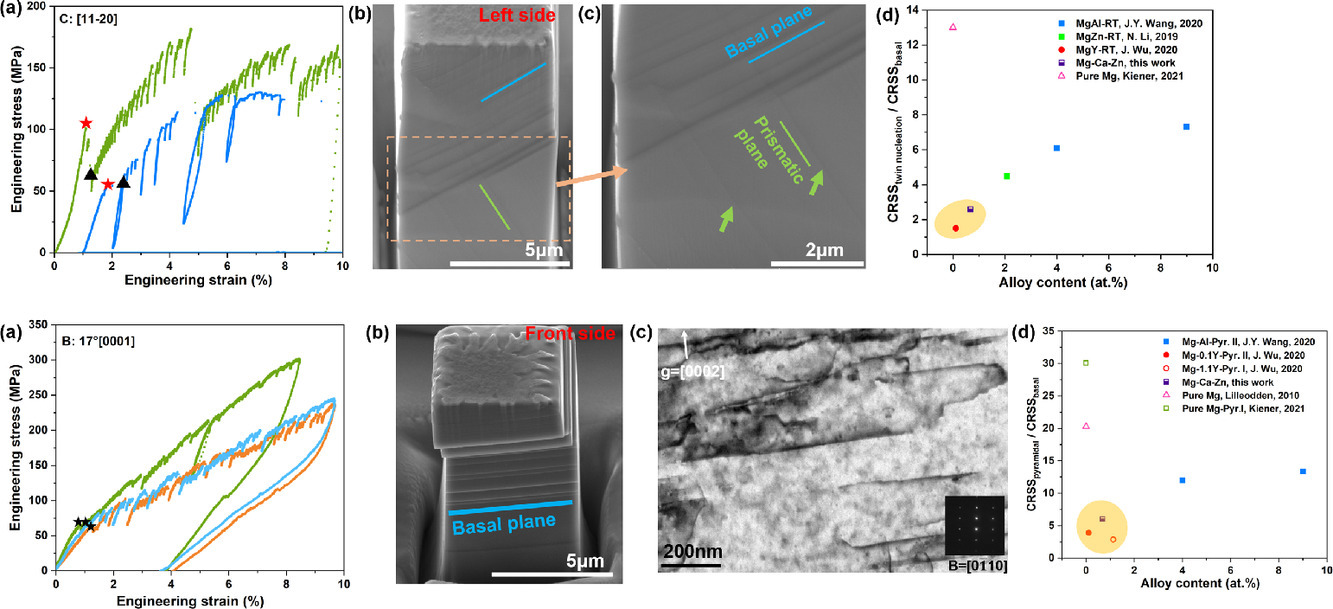
通过对不同取向的单晶微柱进行压缩试验,测量了固溶体中的Ca和Zn对镁合金中基面滑移<a>、压缩孪晶和锥形滑移<c+a>的临界分解剪切应力(CRSS)的影响。与纯Mg相比,溶质原子使基面滑移的CRSS增加到13.5MPa ,而锥形滑移的CRSS低于85MPa,塑性各向异性明显降低。此外,孪晶成核和生长的CRSS非常相似(约37 MPa),而孪晶生长的CRSS值较大,阻碍了热机械加工过程中孪晶的生长。最后,发现了棱形滑移<a>和基面和棱形位错之间的交叉滑移的证据。结果表明,合金塑性各向异性的降低,不同滑移系统和交叉滑移的激活,以及大的CRSS促进孪晶生长的弱基面织构是改善Mg-Ca-Zn合金的延展性和成形性的原因。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117179
12. Stress-sensitive fatigue crack initiation mechanisms of coated titanium alloy
涂层钛合金应力敏感疲劳裂纹萌生机制研究
Yanyun Bai, Tao Guo, Jiawei Wang, Jin Gao, Kewei Gao, Xiaolu Pang✉
Xiaolu Pang: pangxl@mater.ustb.edu.cn, 北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117179
摘要
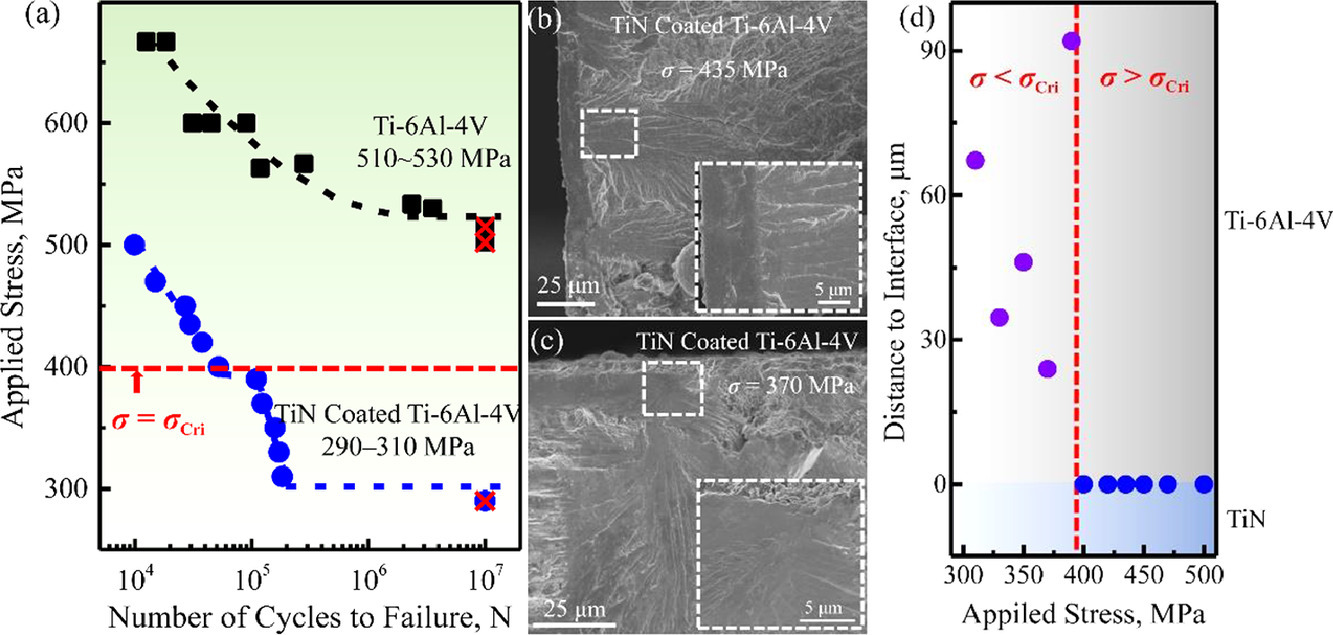
硬质涂层的存在会使金属基体的疲劳寿命降低到一个极低的水平,导致承重结构的灾难性失效。遗憾的是,目前的疲劳裂纹萌生机制很难解释现有的一些实验现象,预防指导理论也仍然缺乏。本研究通过对TiN涂层的Ti-6Al-4V合金进行拉伸-拉伸轴向疲劳实验,发现涂层合金的疲劳裂纹萌发机制对应力敏感,在S-N曲线上呈现出双重特征,这在以往的研究中从未报道过。当施加的应力高于临界应力时,涂层断裂引起的基体解离开裂是疲劳裂纹萌生的原因,导致疲劳裂纹源在界面出现。当施加的应力低于临界应力时,滑移台阶导致涂层断裂,在已经被位错堆积压住的脆性α相上形成额外的应力集中,从而加速了疲劳裂纹在亚表面的萌生。基于所提出的机制,引入了韧性铬夹层以降低涂层裂纹的速度,并吸收从基体脱落的位错,从而使涂层的开裂率的减少从40%增加到20%。本研究提出的机制将为设计硬质涂层提供理论指导,以减少对金属负载结构的疲劳寿命的不利影响,甚至改善基体的疲劳性能。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117176
13. Revealing carbide precipitation effects and their mechanisms during quenching-partitioning-tempering of a high carbon steel: Experiments and Modeling
揭示高碳钢淬火-配分-回火过程中碳化物析出效应及其机理:实验与模拟
Jiazhi Zhang, Zongbiao Dai, Liyang Zeng, Xunwei Zuo, Jianfeng Wan, Yonghua Rong, Nailu Chen✉, Jian Lu✉, Hao Chen✉
Nailu Chen: nlchen@sjtu.edu.cn, 上海交通大学
Jian Lu: jianlu@cityu.edu.hk, 香港城市大学
Hao Chen: hao.chen@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn, 清华大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117176
摘要
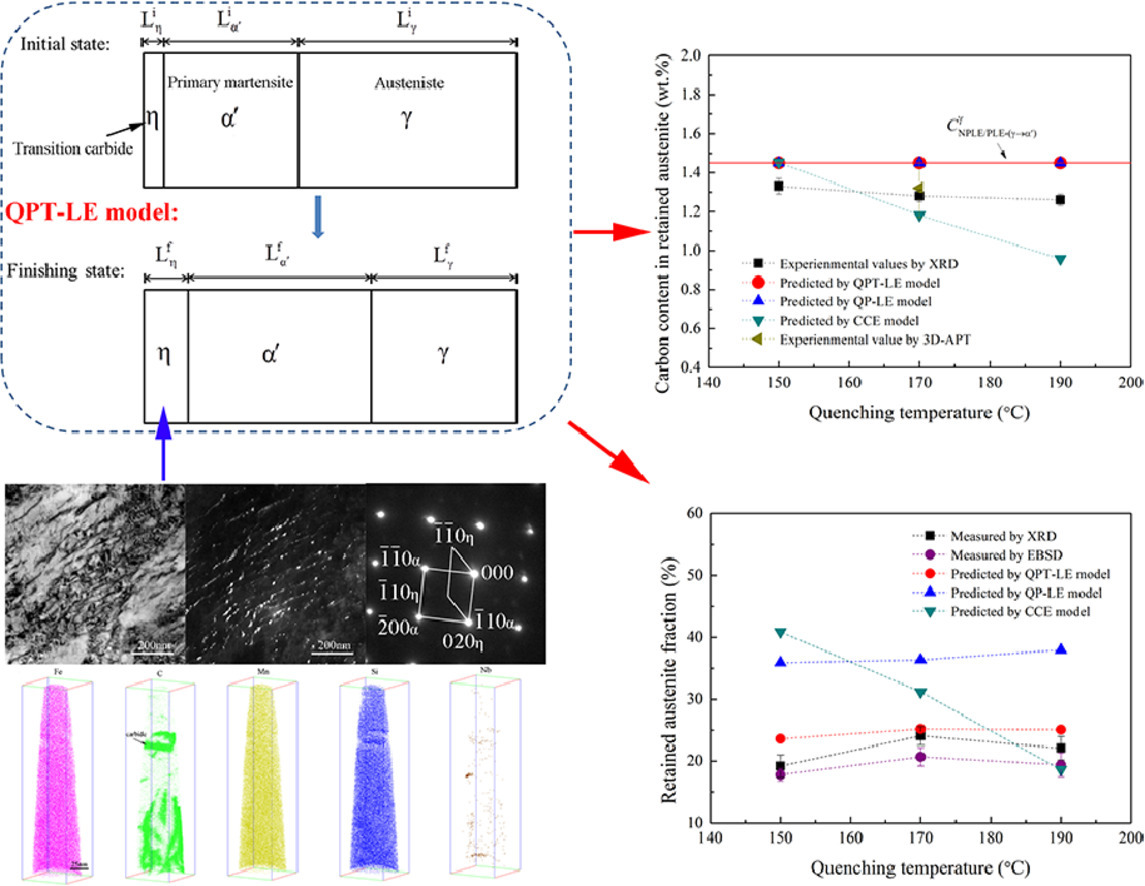
淬火-配分-回火(Q-P-T)工艺,作为淬火和配分(Q&P)的改良工艺,是一种具有良好强度和延展性平衡的超高强度钢的处理工艺。 Q-P-T工艺的本质是在配分过程中通过碳从马氏体到奥氏体的分配来稳定亚稳态奥氏体,并在回火过程中通过微合金碳化物的纳米析出来强化马氏体基体。在配分-回火过程中,会发生碳偏析到位错、过渡碳化物析出和奥氏体分解等竞争性反应,这些反应将对Q-P-T钢的显微组织中发挥重要作用。在本研究中,通过各种工艺对Fe-0.67C-1.48Mn-1.53Si-0.038Nb钢的Q-P-T加工过程中的复杂组织演变进行了系统的表征。基于上述竞争性反应的考虑,建立了一个简明的具有双界面(马氏体/碳化物和马氏体/奥氏体)迁移的QPT-LE(局部平衡)热动力学模型来预测奥氏体分数及其碳含量的演变。这与CCE(受限碳平衡)热力学模型和QP-LE热动力学模型不同,在QPT-LE 模型中引入了碳化物析出的影响。因此,QPT-LE模型可以用来揭示碳化物析出对残余奥氏体分数及其碳含量的影响,而通过考虑碳偏析对位错的影响可以进一步提高碳化物分数的预测精度。总的来说,与流行的CCE模型和QP-LE模型相比,QPT-LE模型可以更好地预测实验结果。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117148
14. Insights into the selection mechanism of Widmanstätten growth by phase-field calculations
通过相场计算深入了解Widmanstätten生长的选择机制
H. Lebbad, B. Appolaire✉, Y. Le Bouar, A.Finel
B. Appolaire: benoit.appolaire@univ-lorraine.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117148
摘要
本研究用相场计算研究了金属合金中Widmanstätten 结构的生长。结果表明,与剪切主导的转变相关的弹性能各向异性足以在恒定过饱和度下产生具有恒定伸长率的板状或针状析出物。进一步结果表明,即使在考虑到弹性的情况下,Ivantsov分析解决方案仍然可以很好地估计尖端周围扩散通量。仔细的分析表明,对于剪切主导的转变,(i)伸长方向位于由弹性核的最小值之一决定的习惯平面内;(ii)尖端形状和尺寸是平衡特征 ,由弹性力驱动,而不是像通常假设的那样由动态决定;(iii)针状析出物的尖端尺寸可以通过伸长方向的弹性核的取值来合理化。

ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117177
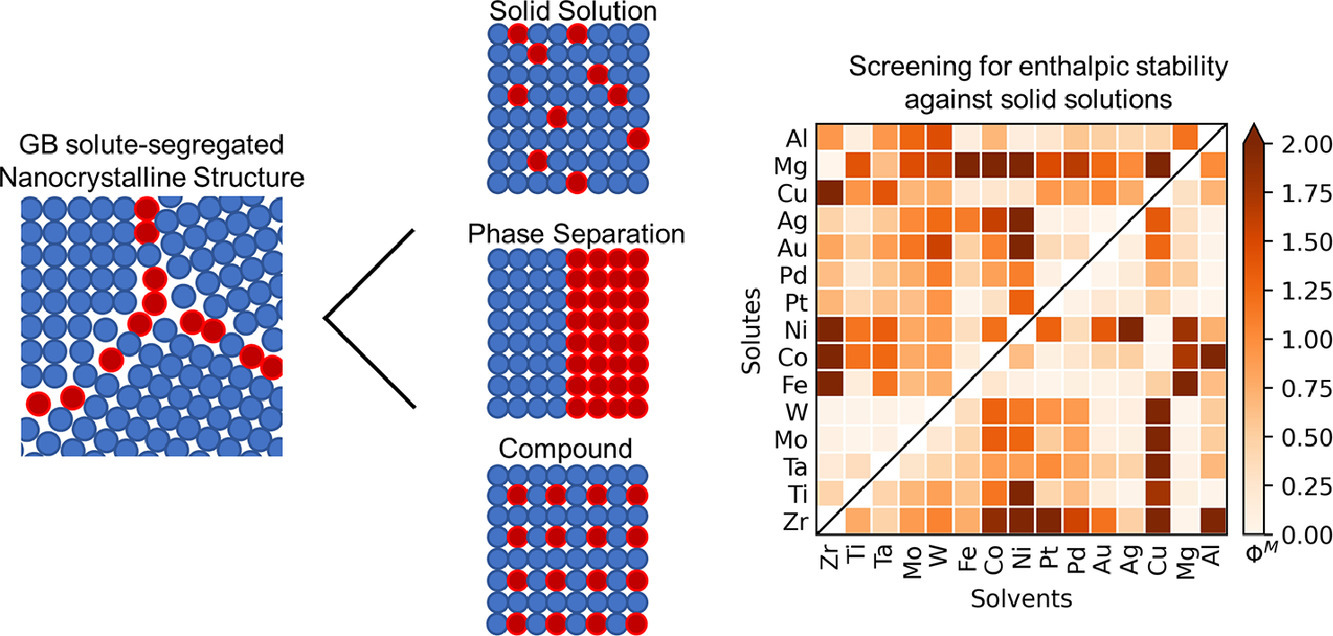
15. Thermodynamics and design of nanocrystalline alloys using grain boundary segregation spectra
基于晶界偏析光谱的纳米晶合金热力学及设计
Malik Wagih, Christopher A. Schuh✉
Christopher A. Schuh: schuh@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.11717
摘要
溶质在晶界(GBs)的偏析是稳定纳米晶合金的一个关键机制。迄今为止,设计和筛选纳米晶稳定性的标准方法使用了一种简化的表示,将GB网络视为单一实体,因此,使用单一的 平均偏析能来表征合金中溶质GB偏析的特征。然而,这种简化没有捕捉到GBs的高度各向异性,这导致了偏析能量的光谱可能非常宽。本研究中我们消除了这种简化,并更正式地概述了正确的热力学标准,以筛选多晶结构的热力学稳定性,说明了 GBs的光谱性质。本研究继续应用所开发的标准来筛选超过200种基于嵌入原子方法潜力的合金组合。在其优点中,这种光谱方法能够严格执行热力学第三定律,而平均偏析能则不能。而且筛选的结果与实验观察结果基本一致。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117149
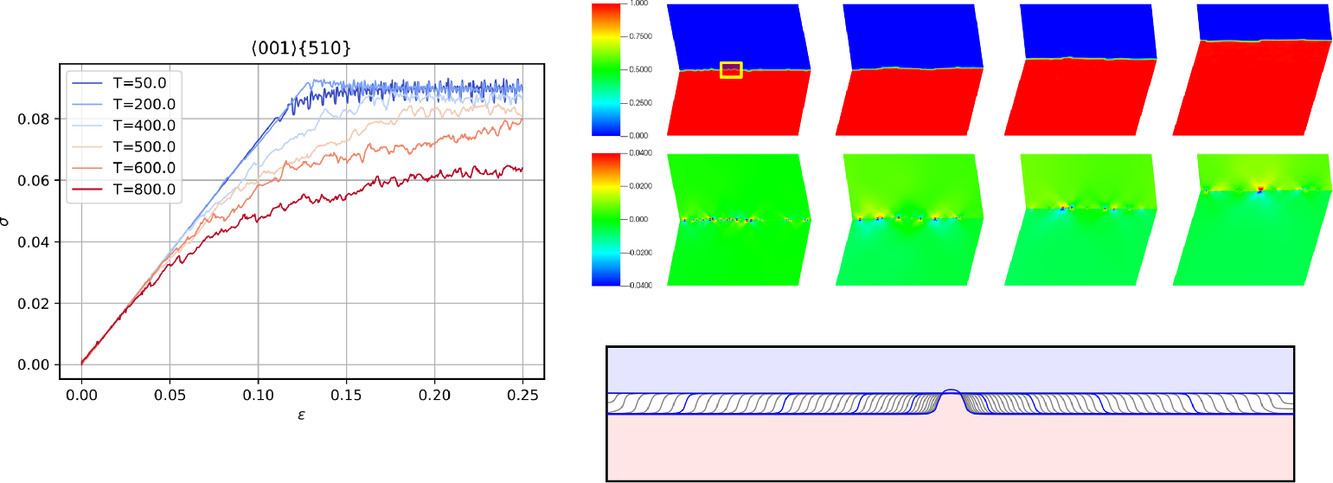
16. Multiphase field modeling of grain boundary migration mediated by emergent disconnections
由断裂介导的晶界迁移的多相场模拟
Mahi Gokuli, Brandon Runnels✉
Brandon Runnels: brunnels@uccs.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117149
摘要
有关晶界迁移的知识是理解和最终调节多晶材料特性的先决条件。来自实验和分子动力学(MD)模拟的证据表明,断裂的形成和运动是晶界迁移的一种机制。在本研究中晶界迁移是使用基于非凸边界能量的最小耗散势原理的多相场模型,以及断裂对的热成核的随机模型来建模的。在这个模型中,断裂在弹性驱动力的存在下自发产生,其运动介导了边界迁移。这种效应是由于断裂对的形成导致了应力集中,使弹性驱动力超过了阈值,并驱动断裂沿界面的扩展。该模型被应用于研究不同温度下单个断裂对的传播/湮灭、受扰动界面的弛豫以及剪切耦合。结果与目前对断裂的理解是一致的,并且捕捉到了热软化的影响。
ACTA
Vol. 217,15 Sep. 2021, 117180
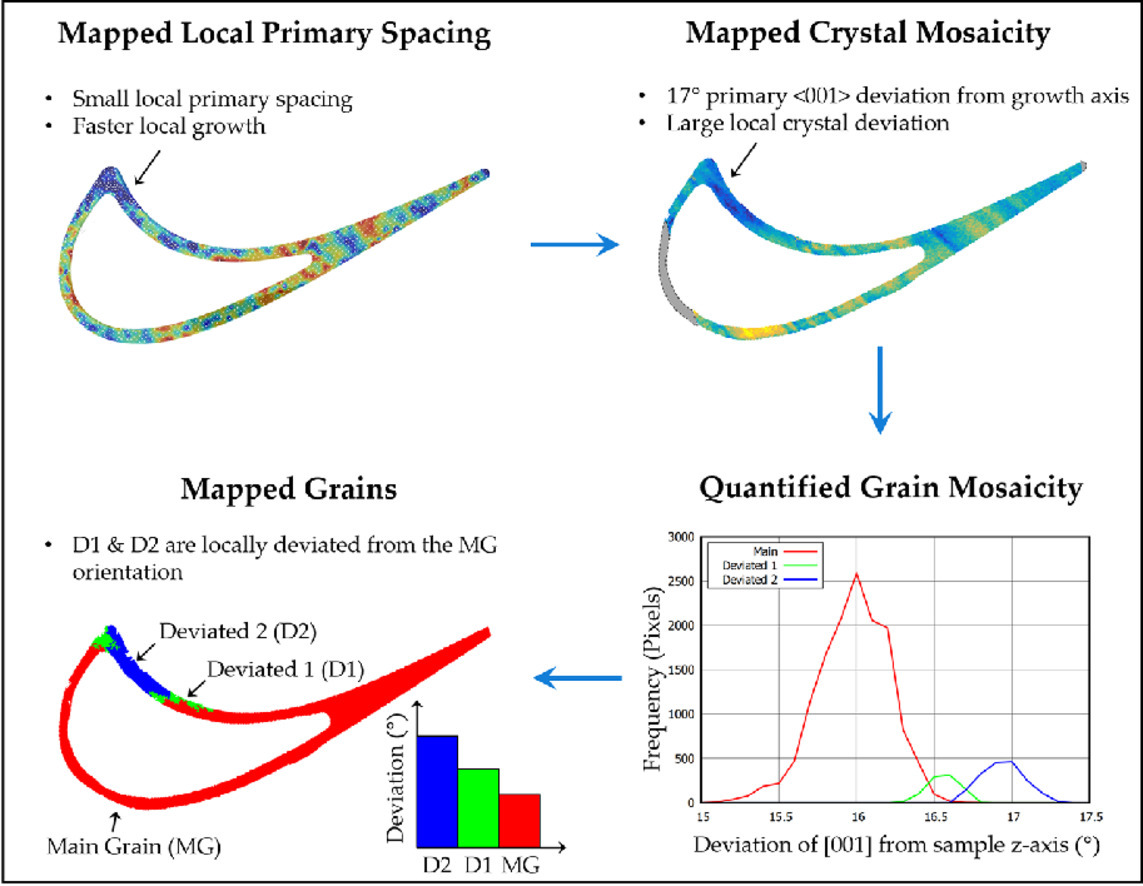
17. On the origin of mosaicity in directionally solidified Ni-base superalloys
定向凝固镍基高温合金镶嵌现象的起源
Joel Strickland✉, Bogdan Nenchev, Karl Tassenberg, Samuel Perry, Gareth Sheppard, Hongbiao Dong, Ruiyao Zhang, Genoveva Burca, Neil D'Souza
Joel Strickland: joel_strickland@hotmail.co.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117180
摘要
本文讨论了引起镶嵌性的小角度晶界的形成,这一现象最近才在单晶镍基超合金领域受到关注。在本文中,采用了先进的显微镜表征技术,从单晶涡轮叶片的横向截面上推断出枝晶的尖端生长动力学。等温曲率在诱导平行于凝固前沿的横向宏观偏析方面的作用已经成为可能。利用飞行时间能量分辨中子成像的晶体学数据和新的Bragg-dip后处理,建立了横向宏观偏析诱导小角度晶界,从而在单晶镍基超合金中产生了镶嵌性。镶嵌性与局部一次晶间距表现出良好的相关性,与那些生长速度较慢的枝晶相比,生长速度较慢的枝晶与铸造方向的<001>偏差更大。鉴于这些发现,本研究进一步讨论了镶嵌性的起源及其对二次晶粒形成的影响。